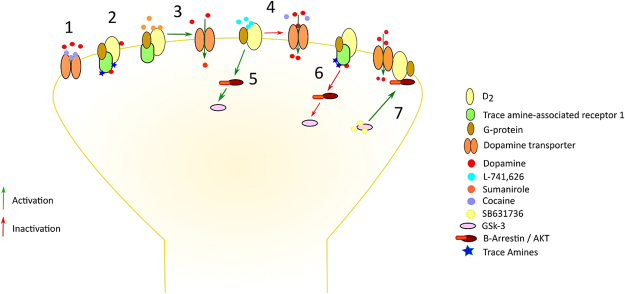
Figure 6.
Proposed mechanism of TAAR1’s role in modulating dopamine (DA) transmission fluctuations induced by cocaine. Cocaine blocks dopamine transporter (DAT) function and thus inhibits DA reuptake by binding to the DAT (1). The DA D2 receptor is a G-protein-coupled receptor, which, when attached to TAAR1 can form a heteromeric complex52. This complex potentiates DA D2 receptor-mediated pre-synaptic autoinhibition and inhibits DA D2 receptor-mediated post-synaptic signalling. As a sentinel system, TAAR1 is sensitive to shifts in DA concentrations and promotes DA homeostasis (2). Sumanirole, a DA D2 receptor agonist causes a similar inhibition of cocaine-induced changes in DA uptake (3) and the antagonist L-741,626 potentiates cocaine-induced effects on DA clearance (4). DA D2 receptor stimulation activates GSK-3 β-arrestin2-dependent pathway (5) and the TAAR1/DA D2 receptor heteromeric complex inhibits GSK-3 through the same pathway (6). Thus, inhibiting GSK-3 with SB631736 activates AKT, which is bound to D2/DAT complex53, increasing DA reuptake (7).