Figure 4.
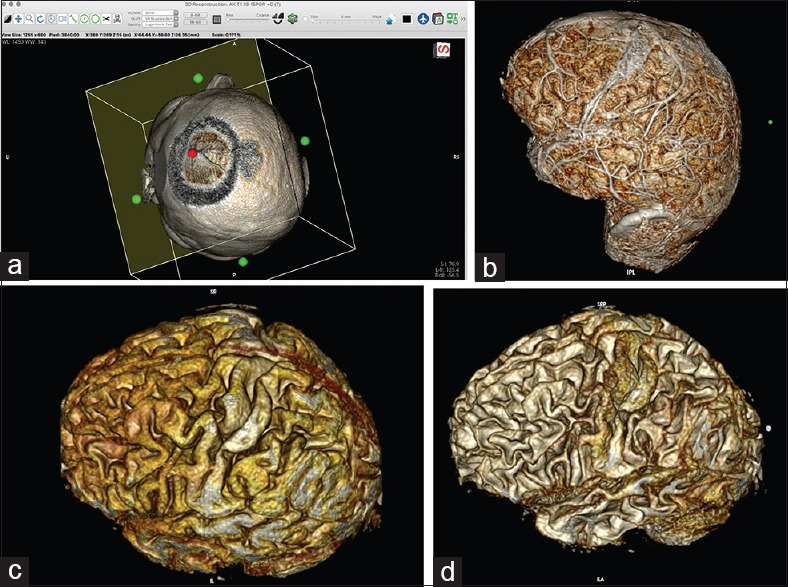
(a) Simulation of the craniotomy window in the 3D viewer with the cropping cube. By clicking on the green dot on the wall of the cube and by gradually reducing the size of the wall, the surgeon can simulate a craniotomy window into a superficial brain lesion. (For details, see video 5.) (b) Images of the brain after skin and bone removal. (For details, see video 6.) The images are generated from 1-mm-thick 3D T1 turbo fast echo MRI slices, with contrast enhancement; the technique allows for visualization of the associated vessels. (c) Images generated from 1-mm-thick 3D T1 turbo fast echo MRI slices, without contrast. The images look more like that of an anatomical specimen. (d) Adjusting the image to the desired level of visualization (⌥ (option key) + left mouse key) allows for decreasing the thickness of the gyri; the technique is useful in planning a microsurgical approach to deep-seated lesions
