Fig. 15.
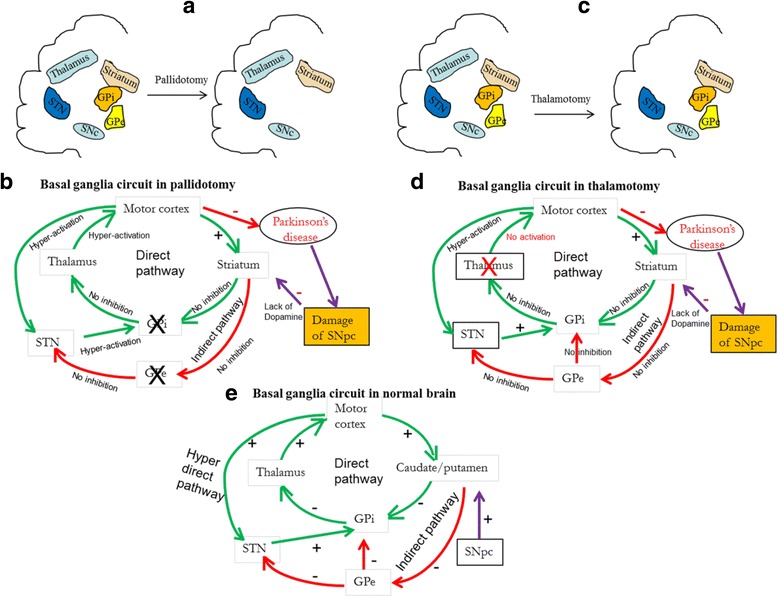
Schematic diagram showing pallidotomy (a), and thalamotomy (c) and the basal ganglia circuitory during pallidotomy (b) and thallatomy (d). In case of pallidotomy, the globus pallidus (GP) is surgically destroyed. In the case of a thalamotomy, both thalami are destroyed surgically, which causes a loos of thalamic excitation to the motor cortex, which can decrease Parkinson-like symptoms. Scematic diagram of basal ganglia circuitory in normal brain is shown in “e”
