Table 2. Optimization of reaction conditions a .
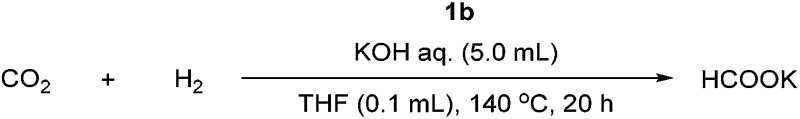
| ||||
| Entry | P(H2)/P(CO2) (atm) | KOH (M) | Yield b (%) | TON c (×103) |
| 1 | 30/30 | 1 | 81 | 81 |
| 2 | 20/20 | 1 | 35 | 35 |
| 3 | 40/20 | 1 | 99 | 99 |
| 4 | 50/10 | 1 | 99 | 99 |
| 5 d | 40/20 | 1 | 20 | 200 |
| 6 d | 40/20 | 2 | 34 | 340 |
| 7 d | 40/20 | 5 | 45 | 450 |
aGeneral reaction conditions: 5 mL aqueous KOH solution, 0.001 mol% iridium catalyst 1b relative to KOH in 100 μL THF, under the desired CO2 : H2 pressure, 140 °C, 20 h.
bYield, which represents conversion of the added KOH, based on 1H NMR analysis with sodium 3-(trimethylsilyl)-1-propanesulfonate as an internal standard.
cTON = turnover number; number of moles of product formed per mole of catalyst.
dCatalyst loading was 0.0001 mol% relative to KOH.
