Figure 1.
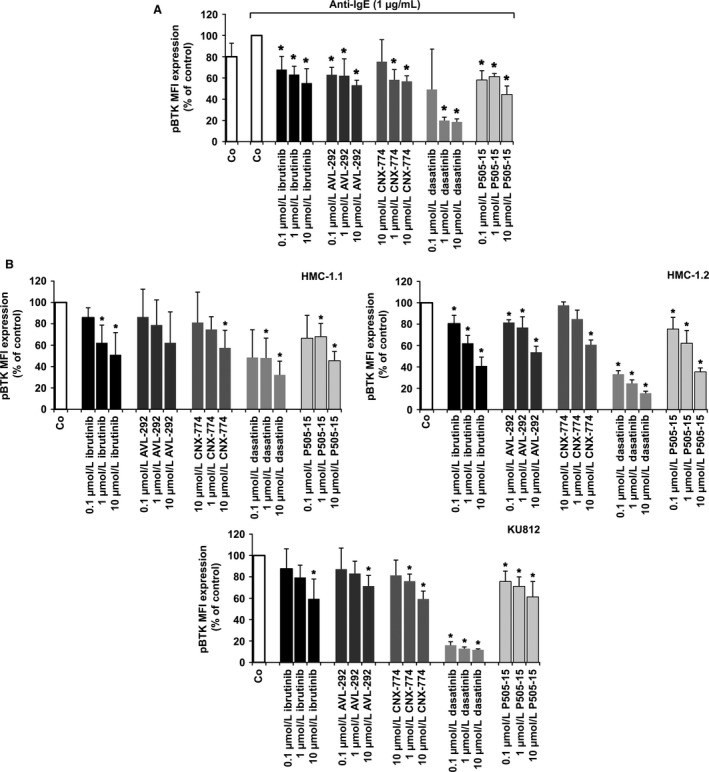
Effects of ibrutinib on expression of pBTK in primary activated human basophils (BA), HMC‐1 cells, and KU812 cells. (A) BA‐containing mononuclear cells (MNC) were incubated in control medium (Co) or in medium containing dasatinib, ibrutinib, AVL‐292, CNX‐774, or P505‐15 (each 0.1‐10 μmol/L) at 37°C for 15 minutes. Then, cells were incubated with anti‐IgE at 37°C for 15 minutes and incubated with a PE‐labeled mAb against CD203c for 15 minutes. Then, cells were permeabilized and stained with an antibody against phosphorylated (p) BTK (pBTK) (phosphorylation site: Y223) as described in the text. Expression of intracellular targets was quantified by multicolor flow cytometry on a FACSCalibur. BA were identified as CD203c‐positive cells. Results show the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of pBTK expression (% of control) and represent mean±SD from three independent experiments. Asterisk (*) P<0.05 by Student's t test with Bonferroni correction. (B) HMC‐1.1 cells (upper left panel), HMC‐1.2 cells (upper right panel), and KU812 cells (lower panel) were incubated with control medium (Co) or medium containing ibrutinib, AVL‐292, CNX‐774, dasatinib, or P505‐15 (0.1‐10 μmol/L) at 37°C for 4 hours. Thereafter, cells were permeabilized and stained with an antibody against pBTK (Y223). Expression of phosphorylated (p) signaling molecules in HMC‐1 and KU812 cells was determined by flow cytometry. Results show MFI values expressed as percentage of control and represent the mean±SD from three independent experiments. Asterisk (*): P<0.05 by Student's t test with Bonferroni correction
