Fig. 5.
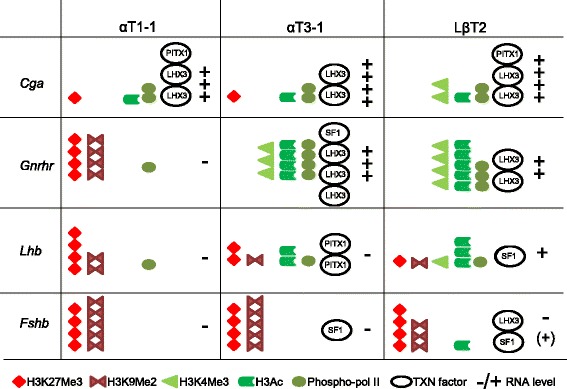
Summary of gonadotrope gene transcription, transcription factor occupancy and chromatin changes in gonadotrope cells. During gonadotrope maturation, illustrated here by the progenitor αT1–1, immature αT3–1, and mature LβT2 cells, the chromatin status changes from a closed conformation on Gnrhr, Lhb and Fshb (enrichment in H3K27Me3 and H3K9Me2) in αT1–1, to a more open conformation in LβT2 cells (increase in H3Ac, and H3K4Me3), which is associated with enhanced expression of Lhb and Gnrhr (+). The progressive opening of the Lhb promoter allows recruitment of the transcription factors (TXN factors) PITX1 and SF1 [68], whereas opening of the Gnrhr promoter allows recruitment of SF1 and LHX3 [69]. The regulatory region of the α-subunit Cga is in an open confirmation during all the stages of maturation, and associated with recruitment of PITX1 and LHX3 and high mRNA expression (+++). The discrete opening of the Fshb promoter during gonadotrope maturation allows association of SF1 and LHX3 to the regulator region of Fshb [70, 71]. Depending on study conditions, Fshb transcript is undetectable or can be detected at low levels in LβT2 cells
