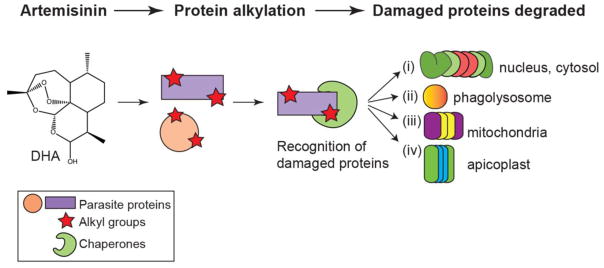
Fig. 1. Artemisinin, its derivatives, and the synthetic ozonides cause widespread protein damage that induce stress pathways.
Treatment with dihydroartemisinin (DHA), the active metabolite of artemisinin (ART), leads to non-specific protein alkylation. Damaged proteins are recognized by chaperones, and targeted for degradation by one of four pathways: (i) the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), (ii) autophagy, (iii), the PfClpY/Q protease, or (iv) the PfClpC/P protease. The subcellular locations of these pathways are denoted to the right of each proteolytic system.