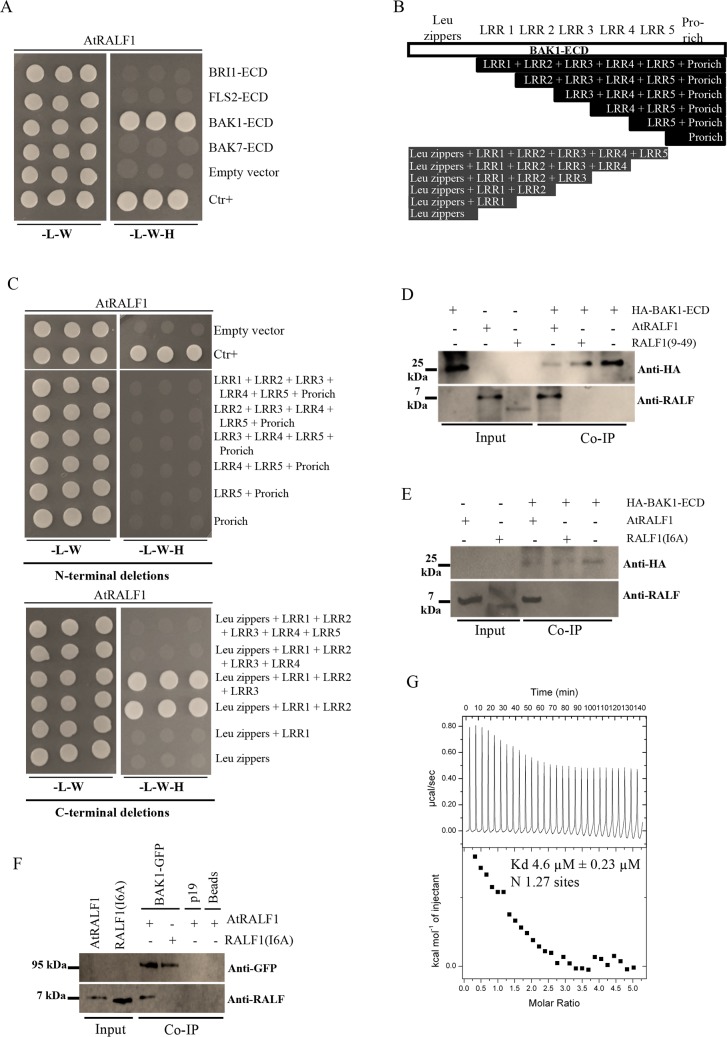
Fig 6. AtRALF1 interacts physically with BAK1 protein.
(A) The active AtRALF1 peptide interacts with the extracellular domain (ECD) of BAK1 (BAK1-ECD) in yeast. The AtRALF1 protein fused to the GAL4 DNA-binding domain (AtRALF1-pGBKT7) was used as bait to test its interaction with the extracellular domain of the proteins fused to the GAL4 activation domain (pGADT7): BAK1 (BAK1-ECD), BAK7 (BAK7-ECD), BRI1 (BRI1-ECD) and FLS2 (FLS2-ECD). (B) Blueprint showing the truncated proteins from the extracellular domain of BAK1 tested in the two-hybrid assay. The extracellular domain of BAK1 comprises leucine zippers (LZ), 5 leucine rich-regions (LRRs) and a proline-rich region (pro-rich). (C) AtRALF1-pGBKT7 was used as bait to test its interaction with truncated proteins fused to the GAL4 activation domain (pGADT7). The transformed yeast cells in (A) and (C) were selected on a synthetic complete medium lacking leucine, tryptophan and histidine to test interactions. (D, E) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) in vitro between the extracellular domain of BAK1 (HA-BAK1-ECD) and AtRALF1 recombinant purified proteins. HA-BAK1-ECD was detected with an anti-HA antibody. AtRALF1 was detected with an anti-RALF antibody. (F) Recombinant AtRALF1 is co-immunoprecipitated with the BAK1-GFP protein expressed in tobacco. BAK1-GFP was detected with an anti-GFP antibody. The synthetic and inactive peptides RALF1(9–49) and RALF1(I6A) did not co-immunoprecipitate with BAK1. (G) Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) of the extracellular domain of BAK1 (BAK1-ECD) vs. AtRALF1 in ITC buffer (15 mM HEPES, pH 6.8). ITC experiments were simulated using 28 injections of BAK1-ED (0.7 mM, vol 10 μL) on AtRALF1 (0.03 mM vol cell = 1.4 mL) at 25°C. Kd = dissociation constant; N = number of binding sites.