Figure 2. Driving 40 Hz oscillations optogenetically in hippocampus reduces A β in 5XFAD mice.
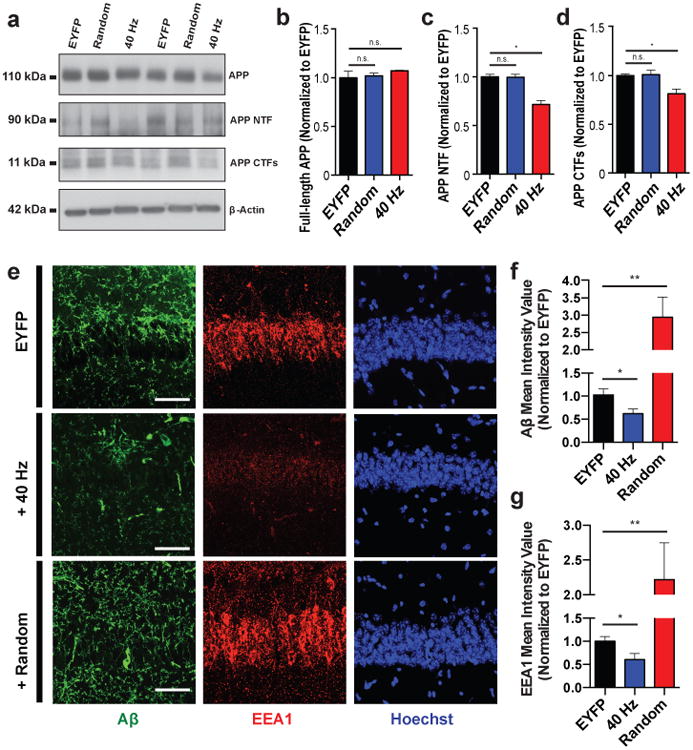
a) Representative western blot showing levels of APP (CT695), APP NTFs (A8967), APP CTFs (CT695), and β-Actin (A5316, loading control) in CA1 of 5XFAD/PV-Cre mice expressing only EYFP or ChR2 with 40 Hz, or random stimulation conditions. 1 mouse per lane, 2 biological replicates. b) Relative immunoreactivity of full-length APP normalized to actin (for b-d, n=6 mice per group). c) Relative immunoreactivity of APP NTF normalized to actin. d) Relative immunoreactivity of APP CTFs normalized to actin. e) Immunohistochemistry with anti-A β (D54D2, green) and anti-EEA1 (610457, red) antibodies in CA1 of 5XFAD/PV-Cre mice (scale bar = 50 μm). f) Relative immunoreactivity of A β normalized to EYFP controls(for f, g, n=3 mice per group). g) Relative immunoreactivity of EEA1 normalized to EYFP controls. n.s. not significant, * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, by one-way ANOVA; mean + SEM in bar graphs.
