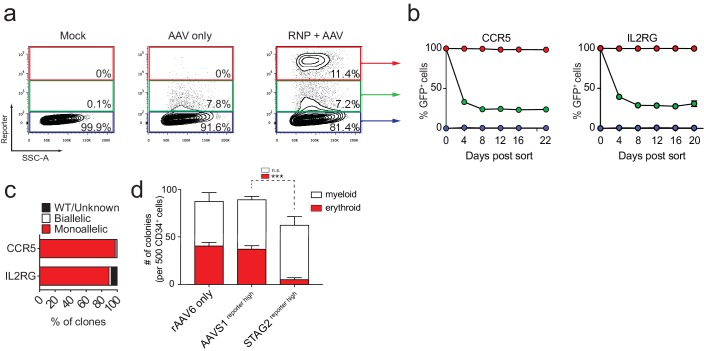
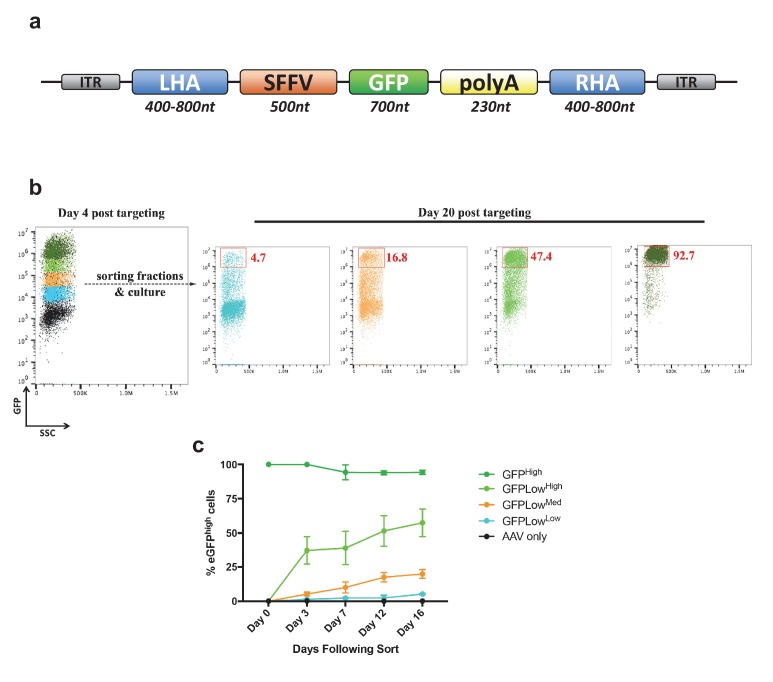
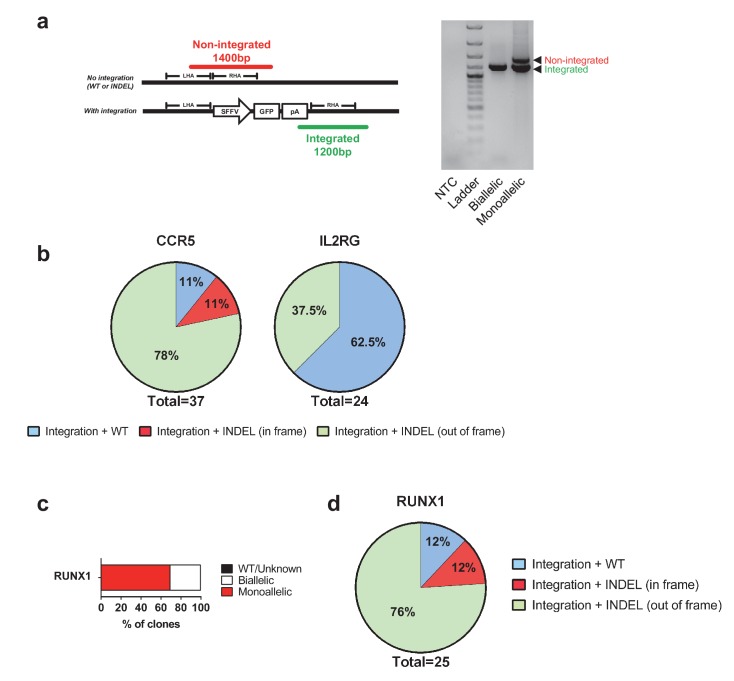
Figure 1. FACS-based identification and enrichment of monogenic genome-edited CD34+ human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs).
(a) HSPCs were electroporated with CCR5-RNP and transduced with CCR5-tNGFR rAAV6 HR donor. Representative FACS plots from day four post-electroporation highlight the CCR5 tNGFRhigh population (red gate) generated by the addition of Cas9 RNP compared to cells with low reporter expression (green gate) and reporternegative cells (black gate). Numbers reflect percentage of cells within gates. (b) Day four post-electroporation, CCR5 (tNGFR or GFP) and IL2RG (GFP)-targeted HSPCs from reporterhigh (red), reporterlow (green), and reporterneg (blue) fractions were sorted and cultured for 20-22 days while monitoring the percentage of cells that remained GFP+. Error bars represent S.E.M. N = 6 for CCR5, N = 3 for IL2RG, all from different CD34+ donors. (c) HSPCs were targeted at CCR5 (with GFP or tNGFR donor) or at IL2RG (GFP donor; only female cells for IL2RG). At day four post-electroporation, reporterhigh cells were single-cell sorted into methylcellulose for colony formation. PCR was performed on colony-derived gDNA to detect targeted integrations. 338 CCR5 and 177 IL2RG myeloid and erythroid methylcellulose colonies were screened from at least two different CD34+ HSPC donors. (d) HSPCs were targeted at the STAG2 gene or the AAVS1 locus with a GFP reporter cassette. Cells that only received the STAG2-GFP AAV6 donor and not Cas9 RNP were included as an additional control. At day four post-electroporation and transduction, reporterhigh cells from the STAG2 and AAVS1 targeting experiments and bulk cells from the STAG2 AAV6 only population were plated in methylcellulose for colony formation. After 14 days, colonies were scored as either erythroid or myeloid based on morphology. Error bars represent S.E.M, N = 3, ***p<0.001, n.s. = p≥0.05, unpaired t-test.