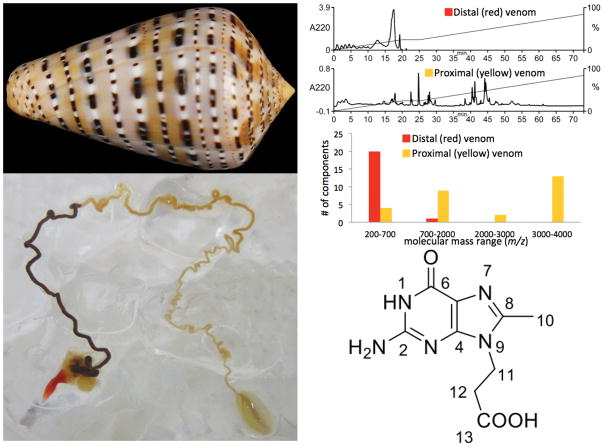
Figure 7.
Analysis of Conus genuanus venom glands. Top left, the shell of Conus genuanus, a worm-hunting species. Lower left, the venom duct of a specimen collected in the Cape Verde Islands; note the red segment close to the pharynx, and the yellowish segment proximal to the venom bulb. Upper right, analysis of the venom by high-performance liquid chromatography and by mass spectrometry. Note that the venom components in the red segment elute earlier on the HPLC column, and have a lower molecular weight, consistent with most of these bing small molecule natural products, and not peptides, which are the major components of the yellowish segment of the venom gland. Lower right, the structure of genuanosine, a bioactive component isolated from the red segment of the venom gland. This unique derivative of guanine has never previously been characterized from any source, and therefore is a unique bioactive natural product, the first small molecule venom component from a cone snail that may be part of its “pre-capture strategy”.