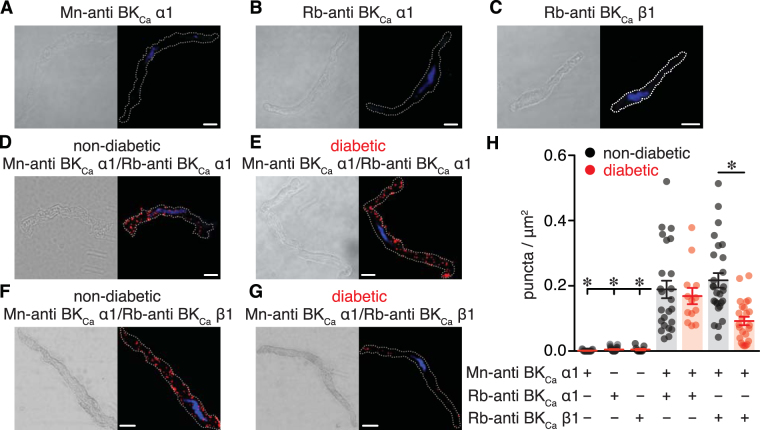
Figure 7.
Decreased association between BKCa α1 and BKCa β1 subunits in vascular smooth muscle cells from diabetic patients. (A–C) Differential interference contrast (DIC) and confocal fluorescent PLA puncta (red) and DAPI (blue) images of freshly dissociated human vascular smooth muscle labeled with mouse-anti BKCa α1 (A), rabbit-anti BKCa α1 (B), and rabbit-anti BKCa β1 (C) antibodies. (D,E) DIC (left) and fluorescence PLA (red)/DAPI (blue) (right) images of dissociated vascular smooth muscle from non-diabetic (D) and diabetic (E) patients co-labeled with two distinct antibodies for the BKCa α1 subunit. (F,G) DIC (left) and fluorescence PLA (red)/DAPI (blue) (right) images of dissociated human vascular smooth muscle from non-diabetic (F) and diabetic (G) patients co-labeled for BKCa α1 and BKCa β1 subunits. Scale bar = 10 μm. (H) Quantification of PLA fluorescent puncta per μm2 cell area for non-diabetic and diabetic vascular smooth muscle cells labeled for mouse-anti BKCa α1 (n = 19 cells), rabbit-anti BKCa α1 (n = 27 cells), rabbit-anti BKCa β1 (n = 12 cells), mouse-anti BKCa α1 + rabbit-anti BKCa α1 (n = 24 non-diabetic, 14 diabetic cells); mouse-anti BKCa α1 + rabbit-anti BKCa β1 (n = 27 non-diabetic, 24 diabetic cells). *P < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test. Significance for columns 1, 2, 3 and 5 was compared to column 4, and column 7 was compared to column 6.