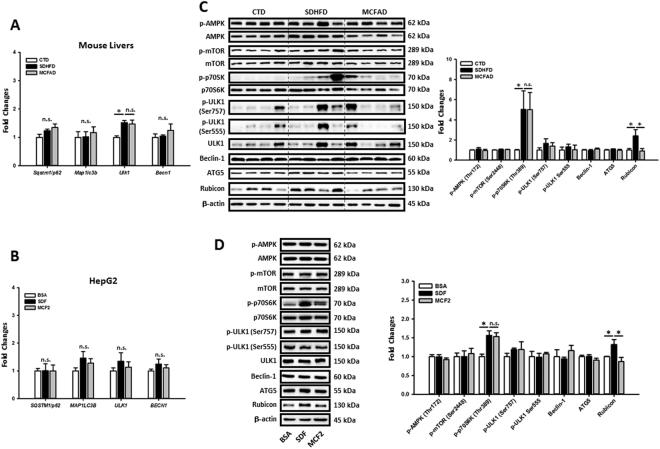
Figure 5.
Increasing MCFA ratio restored hepatic autophagy by downregulating LCFA-induced Rubicon independently of regulating early-stage autophagy signaling pathways. To clarify the molecular mechanisms of MCFAs-protected autophagy, we analyzed the regulations on early-stage and late-stage autophagy signaling pathways in both mouse livers and HepG2 cells. The Sqstm1/p62, Map1lc3b, Ulk1, Becn1, SQSTM1/p62, MAP1LC3B, ULK1, and BECN1 mRNA levels in mouse livers (A) and HepG2 cells (B) were measured using qPCR. The expression of phospho-AMPK (Thr172) phospho-mTOR (Ser2448), phospho-p70S6K (Thr389), phospho-ULK1 (Ser757), phospho-ULK1 (Ser555), Beclin1, ATG5, and Rubicon in HFD-fed mouse livers (C) and fat-loaded HepG2 cells (D) are analyzed using Western blotting. For qPCR, Actb and ACTB mRNA levels were used as the internal controls. For densitometric analyses of Western blotting data, β-actin and total target protein (for phospho-proteins) were used as the loading controls. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 6 and 3 for in vivo and in vitro studies respectively). * P < 0.05. n.s.: no significant difference; SDF: standard fat loading mixture (0.4 mM PA + 0.4 mM OA); MCF2: MCFA-containing fat mixture 2 (0.4 mM PA + 0.2 mM OA + 0.2 mM LA). Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure S5.