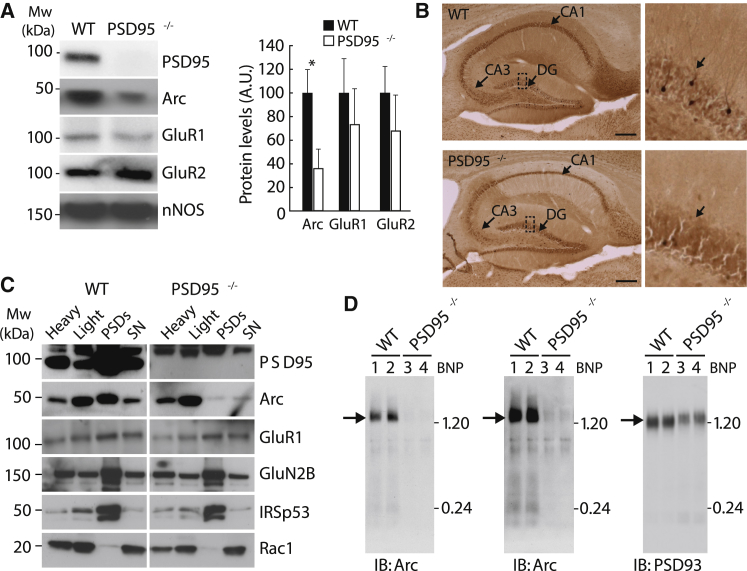
Figure 3.
Arc Protein Levels Are Reduced in Fractions of PSD95 Knockout Mice
(A) Representative immunoblot showing the relative abundance of PSD95, Arc, GluR1, and GluR2 proteins in total hippocampal lysates from PSD95−/− and matched WT littermates. Arc is reduced to 35.0% ± 17.1% of the WT in the PSD95 mutant mice (N = 4 for each matched pair, ∗p < 0.05). Neuronal NOS (nNOS) was used as a loading control.
(B) Representative Arc staining of sagittal sections of the hippocampus (left) and magnification of the granular layer (right) for WT and PSD95 knockout mice. Scale bar, 1 mm.
(C) Hippocampal extracts of PSD95 mutant and WT mutant mice were biochemically fractionated into synaptosomes and into cytoskeletal and vesicular components, referred to as “light.” The synaptosomal fraction was subsequently dissociated into PSDs and Triton X-100 soluble fraction. Arc levels were dramatically reduced in the PSD95 mutant, whereas no changes in GluR1, GluN2B, IRSp53, and Rac1 proteins were observed.
(D) Blue native PAGE (BNP) of WT and PSD95 knockout forebrain extracts blotted with Arc and PSD95 antibodies. Long exposure of the blots shows Arc complexes migrating at a lower molecular weight than 1.20 MDa (center). SN, Triton X-100 soluble fraction.