Figure 10.
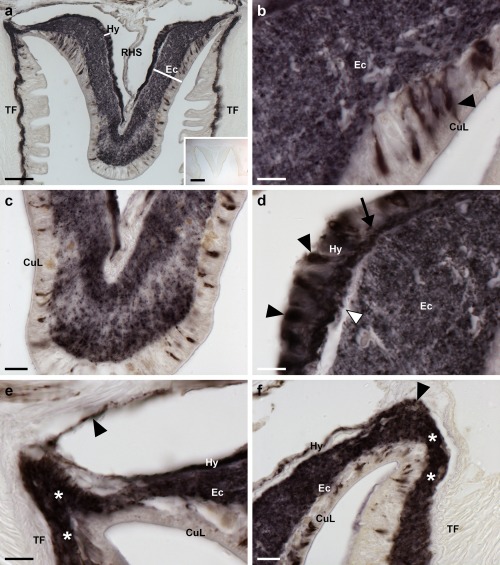
Localization of ArPPLN1b‐immunoreactivity (ArPPLN1b‐ir) in the radial nerve cord of A. rubens. (a) Tranvserse section of a radial nerve cord showing ArPPLN1b‐ir in both the ectoneural and hyponeural regions. The inset of (a) shows absence of immunostaining in a radial nerve cord section incubated with ArPPLN1b antiserum pre‐absorbed with the antigen peptide (ArPPLN1b‐ag), demonstrating the specificity of immunostaining observed with the ArPPLN1b antiserum. (b) High magnification image of the ectoneural region of the radial nerve cord showing immunostained bipolar shaped cells in the sub‐cuticular epithelium (arrowhead) and densely packed immunostained processes in the underlying neuropile region. (c) High magnification image of the ectoneural region at the tip of the V‐shaped radial nerve cord showing layer‐specific variation in the density of immunostained processes. (d) High magnification image showing immunostained monopolar shaped cells (arrowheads) and their stained processes (arrow) in the hyponeural region of the radial nerve cord. The unstained collagenous tissue layer (white arrowhead) that separates the hyponeural region from the densely stained ectoneural neuropile can also be seen here. (e, f) High magnification images showing immunostaining at the junction between the radial nerve cord and an adjacent tube foot. The continuity of immunostaining in the ectoneural region of the radial nerve and in the basiepithelial nerve plexus of the tube foot (asterisks) can be seen here. In (e) the stained process(es) (arrowhead) of a hyponeural neuron(s) can be seen projecting over the roof of the perihemal canal in close association with the transverse infra‐ambulacral muscle. In (f) the stained processes (arrowhead) of hyponeural neurons can be seen projecting to the base of the adjacent tube foot. Abbreviations: CuL, cuticle layer; Ec, ectoneural region; Hy, hyponeural region; RHS, radial hemal strand; TF, tube foot. Scale bars: 50 μm in (a); 200 μm in (a) inset; 10 μm in (b), (d), (e); 20 μm in (c), (f)
