Figure 4.
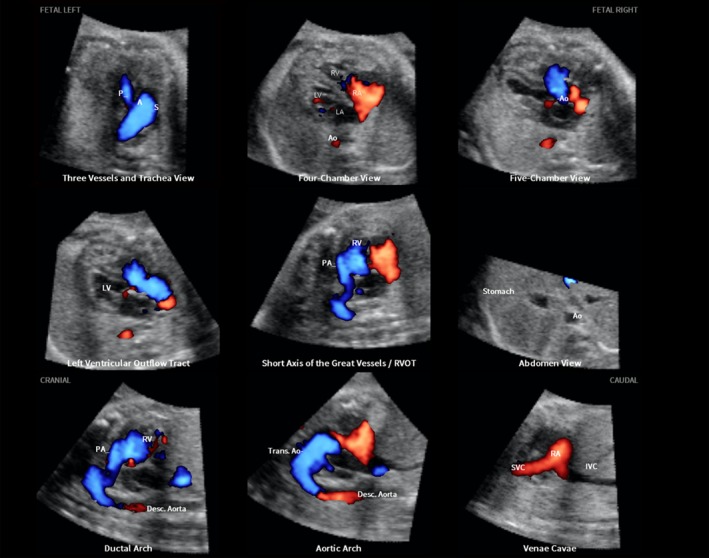
Application of color Doppler Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography method in 31‐week fetus with tetralogy of Fallot (diagnostic planes with automatic labeling shown) (see Videoclip S6). Spatiotemporal image correlation volume acquired with S‐flow Doppler ultrasound. Six echocardiography views were abnormal and demonstrate typical features of this cardiac defect. Three vessels and trachea view shows narrow pulmonary artery due to stenosis, while transverse aortic arch is prominent. There is ‘Y‐shaped’ appearance of great vessels and antegrade flow (blue color) is seen. As is commonly noted in conotruncal abnormalities, four‐chamber view appeared normal, with diastolic perfusion across both atrioventricular valves (see Videoclip S6). Both five‐chamber and left ventricular outflow tract views show overriding aorta, dilated aortic root and perimembranous ventricular septal defect. Shunting of blood is seen from right ventricle across the ventricular septal defect into aortic root (five‐chamber view) and large overriding aorta (left ventricular outflow tract view). In short‐axis view of great vessels/right ventricular outflow tract, pulmonary artery is narrow with small ductus arteriosus and cross‐section of aorta is dilated. Ductal arch demonstrates similar findings. S‐flow Doppler signal was helpful in delineating anatomy of pulmonary artery and ductus arteriosus, as well as confirming antegrade flow in these structures. In aortic arch view, aortic root is dilated and there is prominent ascending aorta. A, transverse aortic arch; Ao, aorta; Desc., descending; IVC, inferior vena cava; LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; P, pulmonary artery; PA, pulmonary artery; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle; RVOT, right ventricular outflow tract; S, superior vena cava; SVC, superior vena cava; Trans., transverse.
