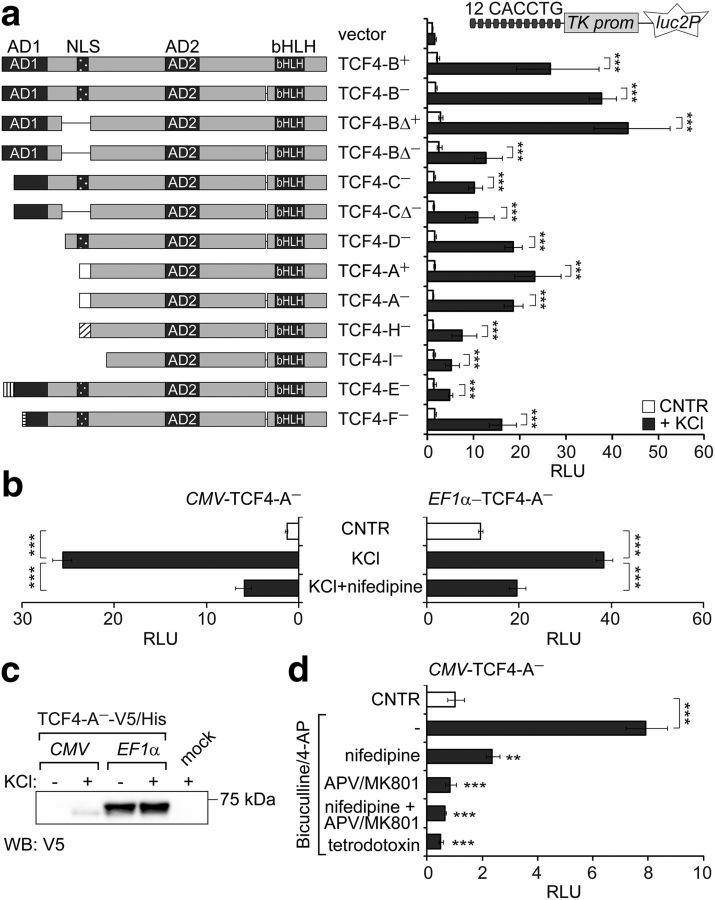
Figure 1.
Identification of TCF4 as a neuronal activity-regulated transcription factor. The effects of membrane depolarization (a, b) and increased synaptic activity (d) on the induction of TCF4-controlled transcription in primary neurons are shown. Rat primary neurons were transfected with TCF4 isoforms encoding vectors, firefly luciferase construct carrying 12 μE5 E-boxes in front of TK promoter, and Renilla luciferase construct with EF1α promoter (a) or PGK1 promoter (b, d). For overexpression of TCF4 isoforms, vectors containing CMV (a, b, d) or EF1α (b) promoter were used. Transfected neurons were left untreated or treated with KCl (a, b) or biculline/4-AP (d) for 8 h. In b and d, tetrodotoxin, nifedipine, or APV/MK801 was used to block action potentials, VGCCs, or NMDARs, respectively. Luciferase activities were measured and data are presented as fold induced levels above the signals obtained from empty vector transfected untreated cells (a, b) or TCF4-A−-expressing untreated cells (d). Shown are the mean results from four independent experiments performed in duplicates. Error bars indicate SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc tests for comparisons across treatment (a) or by Dunnett's post hoc tests for comparisons with cells treated only with KCl (b) or bicuculline/4-AP (d). AD, Activation domain; RLU, relative luciferase units. c, Western blot analysis of C-terminally V5/His-tagged TCF4-A− protein overexpressed from CMV or EF1α promoter in primary neurons left untreated or treated with KCl for 8 h.