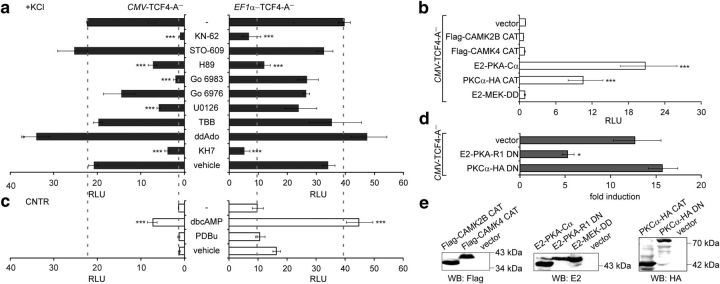
Figure 4.
Identification of signaling pathways involved in the induction of TCF4-dependent transcription by neuronal activity. Shown is the effect of treatment with pharmacological inhibitors (a), coexpression of constitutively active kinases (b), treatment with kinase activators (c), and coexpression of DN kinase subunits (d) on TCF4-A−-mediated transcription. Neurons were transfected with firefly luciferase construct carrying 12 μE5 E-boxes in front of TK promoter, Renilla luciferase construct with EF1α or PGK1 promoter, and TCF4-A− vector with CMV or EF1α promoter, respectively. Constructs coding for various constitutively active and DN protein kinase subunits were cotransfected in b and d, respectively. The transfected neurons were left untreated or treated with the indicated compounds for 8 h. Data are presented as fold induced levels above the signals obtained from empty vector transfected and untreated cells in a–c and as fold induction of luciferase activity in KCl-treated neurons compared with untreated neurons in d. Shown are the mean results from at least three independent experiments (see Materials and Methods for details) performed in duplicates. Error bars indicate SEM. Figures a and c are to scale and dashed lines indicate reporter levels in nontreated and KCl-treated TCF4-A−-expressing cells. Statistical significance shown with asterisks is relative to the first data point in each chart. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc tests. RLU, Relative luciferase units. E, Western blot analysis of constitutively active and dominant negative protein kinase subunits overexpressed in HEK-293 cells.