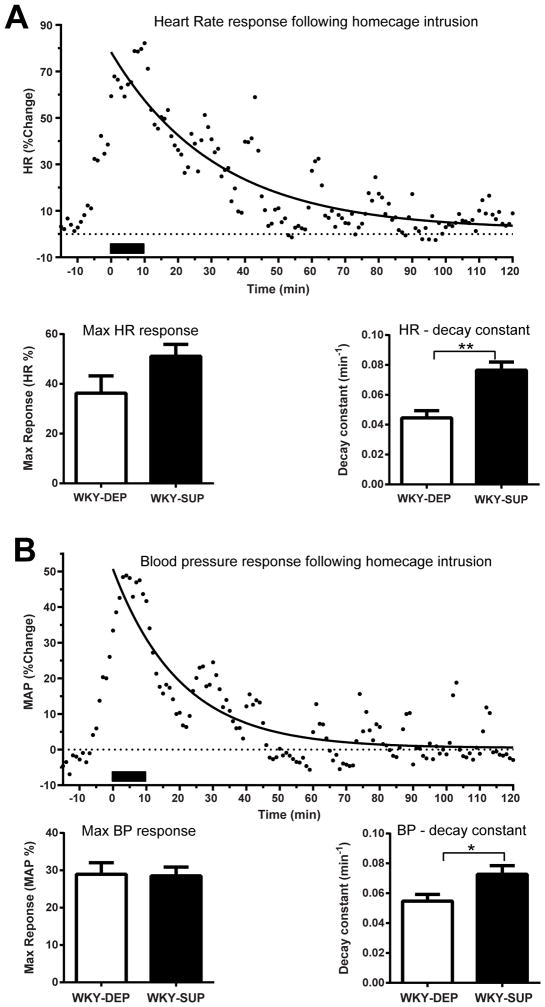
Figure 6.
Dietary methyl donor supplementation decreases WKY rats’ cardiovascular response to acute stress of home cage intrusion. (A) A novel age-matched male intruder rat was introduced into the home cage of each methyl donor supplemented (WKY-SUP) or depleted (WKY-DEP) WKY test rat for 10 min. Maximal heart rate (HR) response was determined by the maximal change in the value from baseline (15 min average prior to the beginning of the test) during the test period. Curve-fitting analysis was also performed to determine HR recovery after stress; solid line indicates curve-fitting analysis in a representative animal. WKY-SUP and WKY-DEP groups displayed similar maximal HR responses to the intrusion, although WKY-SUP rats showed greater HR decay constant, indicating steeper rate of recovery. (B) Similarly, the two groups displayed similar maximal mean arterial pressure (MAP) response to home cage intrusion, with the WKY-SUP rats showing increased MAP decay. *Statistically significant differences at p < 0.05; ** indicates p <0.001.