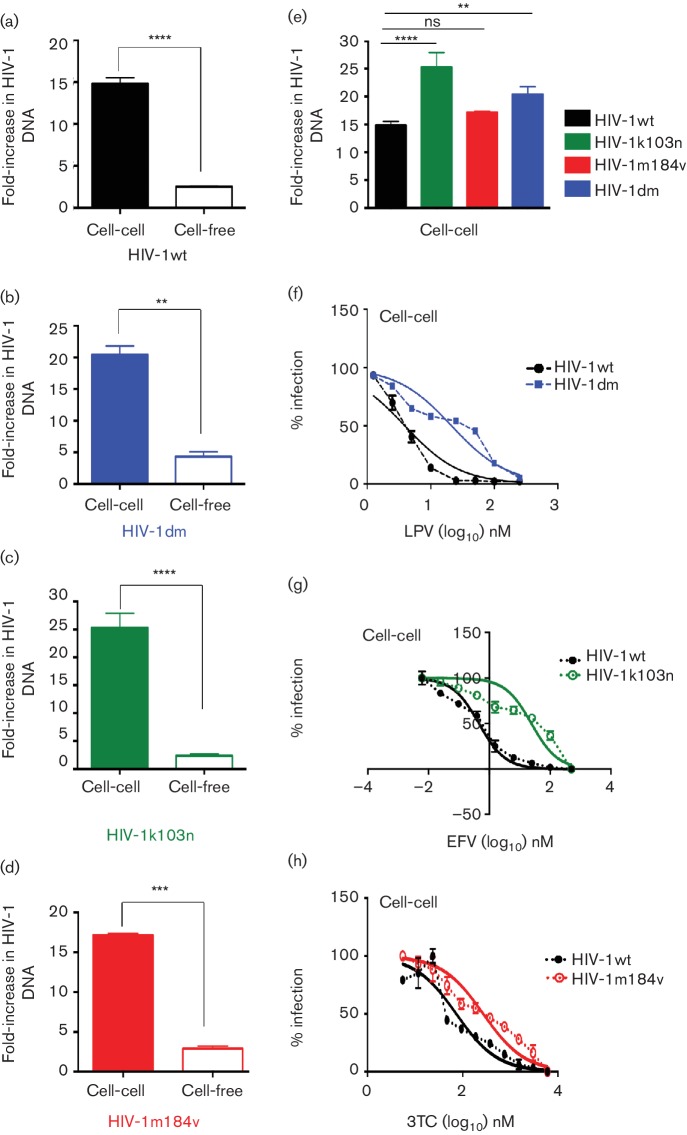
Fig. 4.
Drug-resistant viruses spread efficiently by a cell-to-cell mechanism and maintain their resistant phenotype with this mode of spread. Cell-to-cell spread of (a) HIV-1wt, (b) HIV-1dm, (c) HIV-1k103n and (d) HIV-1m184v was measured and compared to their cell-free spread using a qPCR-based cell-to-cell assay system. All viruses spread efficiently by a cell-to-cell mechanism, with this mode of spread being 5–7 times more efficient for all viruses tested in comparison to cell-free spread. (e) Drug-resistant viruses spread from cell to cell with comparable efficiency to wild-type virus. Drug-resistant viruses (f) HIV-1dm, (g) HIV-1k103n and (h) HIV-1m184v all maintain their resistant phenotype when spreading by a cell-to-cell mechanism. A representative of two independent repeats is shown. Error bars show the standard deviation of the mean. Statistical comparisons were done using a paired Student t-test. ****P<0.0001, ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, ns not significant.