Figure 6. The absence of renal tubular angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) amplifies reductions in abundance and phosphorylation of NaCl cotransporter (NCC) and cleaved (CL) a subunit of the epithelial sodium channel (aENaC) after 3 weeks of a high-salt diet.
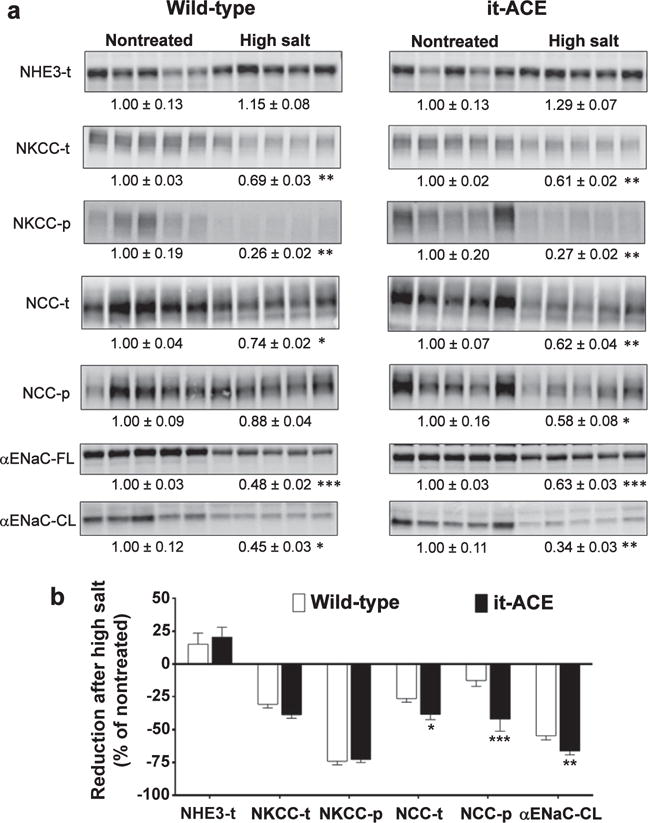
Renal sodium transporter expression was analyzed in total kidney homogenates from nontreated mice and after 3 weeks of high-salt diet. L-NAME was given to wild-type (0.5 mg/ml) and mutant (1.5 mg/ml) mice in the drinking water. Immunoblots of renal cortical homogenates were performed with a constant amount of protein per lane. Relative abundance from each group is displayed below the corresponding blot as mean SEM. (a) n = 5 per group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 versus corresponding nontreated mice. (b) Bars represent the relative reduction versus nontreated mice (set as 0); *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. NHE3, Na+/H+ exchanger 3; NKCC, Na+-K+-2Cl+ cotransporter.
