Figure 1.
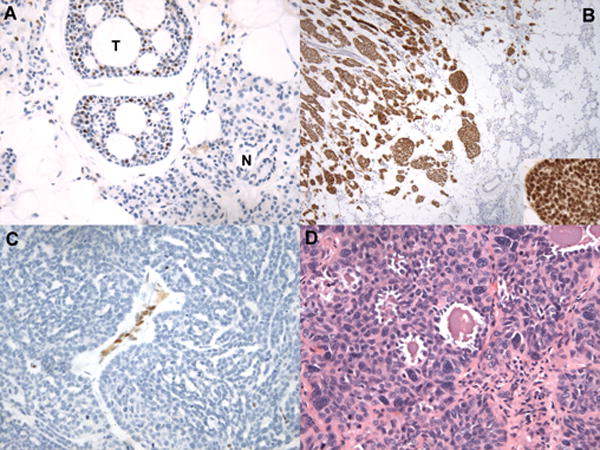
Histologic correlates of NICD1 staining in selected cases diagnosed as ACC. A) NICD1 staining in a tubular/cribriform ACC (hematoxylin counterstain). The field contains several nests of tubular/cribriform ACC showing typical subset NICD1 staining (T) adjacent to normal parotid gland (N), which is NICD1 negative. B) Diffuse NICD1 positivity in a solid ACC. Low-power view demonstrates infiltration of normal salivary gland by an ACC with a solid growth pattern and strong, diffuse NICD1 positivity; note nuclear staining in the high-power inset image. C) Absence of NICD1 staining in a tumor diagnosed as ACC involving the middle turbinate showing a ribbon-like or trabecular to solid growth pattern. Other areas in this tumor showed a tubular/cribriform growth pattern reminiscent of ACC. Note NICD1 staining in endothelial cells, which provide an internal control for immunoreactivity. D) H&E-stained section of a NICD1-negative tumor diagnosed as ACC showing squamoid differentiation and microcystic areas.
