Fig 3. Repair Mechanisms Following Targeted Double Strand Break by Site-Specific Nucleases.
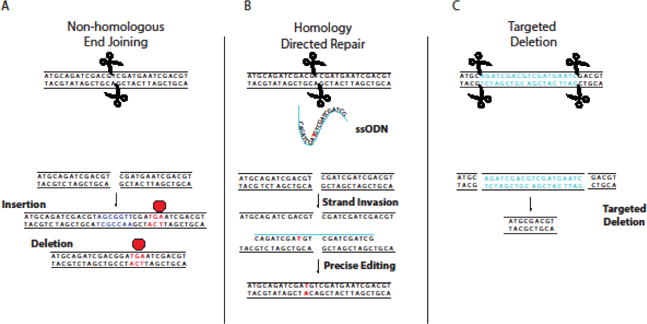
A) Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) can result in repair of dsDNA with random insertions or deletions that may cause frameshift mutations, resulting in premature termination of translation. B) Introduction of a homologous donor sequence (ssODN shown) can facilitate precise editing through homologous recombination repair pathways. C) Use of two nucleases can create specific deletions, allowing the removal of entire regions of the genome.
