Fig. 5.
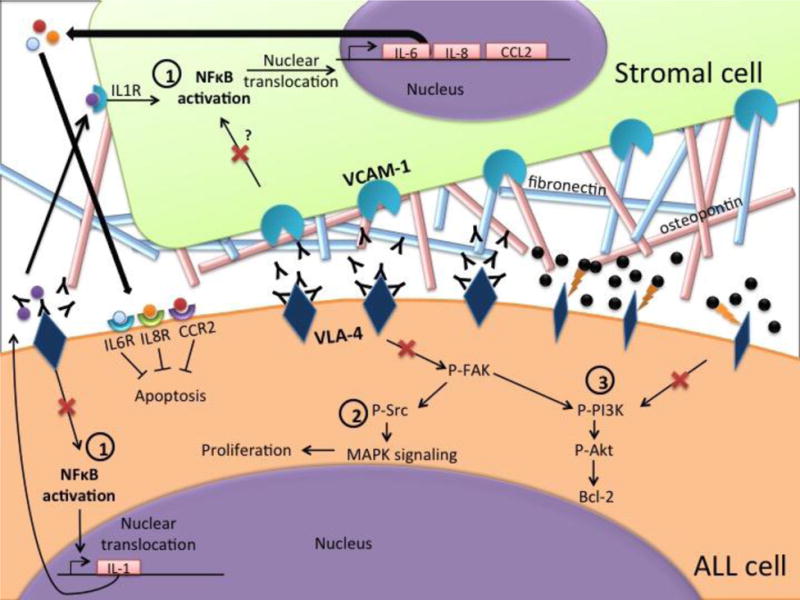
Pictorial representation of the mechanisms of drugs targeting VLA-4. VLA-4 binds to its target VCAM-1 on bone marrow stromal cells or to ECM proteins such as osteopontin and fibronectin. This interaction activates pro-survival signaling pathways such as 1) NF-κb, 2) Src/MAPK and 3) PI3K/Akt. Disruption of these interactions by Natalizumab (Black Ys), a monoclonal antibody that targets VLA-4, or AS101 (black spheres), which oxidizes adjacent thiol residues in the exofacial domain of VLA-4 molecules. This prevents target binding and causes cytoskeletal and conformational changes in the VLA-4 molecule, results in inhibition of these pathways (shown by red crosses).
