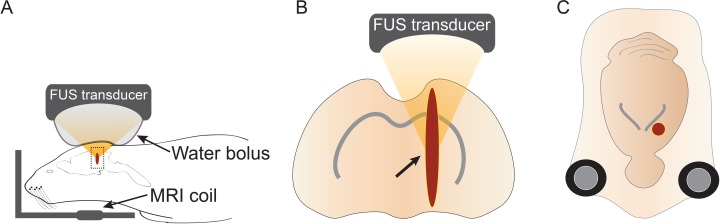
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the focused ultrasound (FUS) exposures. (A) FUS) exposures were provided noninvasively in the brain, where a flexible, acoustically transparent bolus, filled with degassed deionized water and able to deform to the shape of the head, was used to couple the transducer directly to the dorsal region of the head. The head region and the transducer were situated within the magnetic resonance imaging coil inside the magnet bore, which was used for both targeting and monitoring of the exposures. (B) The FUS exposures were targeted at the striatum (arrow), seen in the axial view. However, because of the relatively large size of the long axis of the focal zone of the ultrasound beam to the rat brain, the active region of treatment (dark red) extended from the dorsal cortex to the ventral striatum. (C) Coronal view of the rat brain showing the relative size of the radial diameter of the focal zone. Image not to scale. MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.