Figure 1.
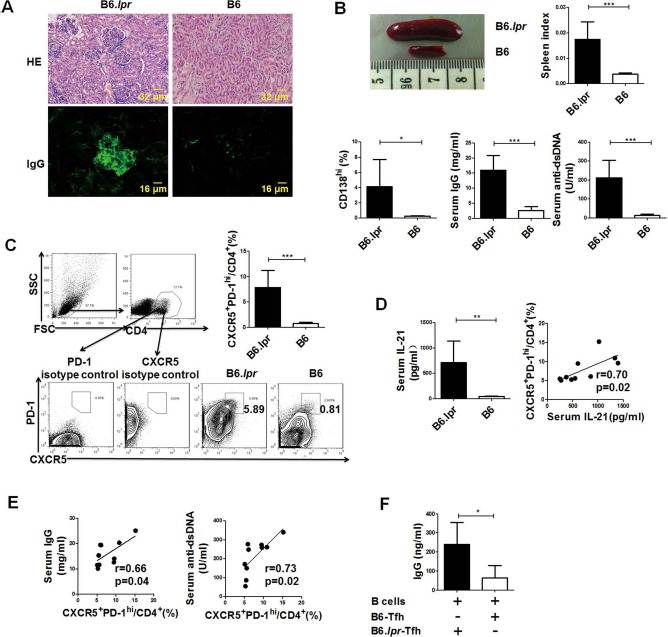
Increased T follicular helper (Tfh) cell proportion contributed to the abnormal B-cell response in B6.lpr mice. (A–E) Female B6.lpr mice (6–8 months old; n = 10) and age- and sex-matched B6 mice (n = 5) were sacrificed. (A) Representative images of kidney hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) sections and immunoglobulin G (IgG) immunostaining. (B) Representative image of spleen, spleen index, frequencies of splenic plasma cells, serum total IgG levels, and anti-double stranded (ds)DNA antibody levels. (C) Gating strategy of C-X-C chemokine receptor 5-positive (CXCR5+) programmed cell death-1 (PD-1)hi Tfh cells and the frequencies of splenic Tfh cells. (D) Serum interleukin-21 (IL-21) concentrations and correlation between the serum IL-21 concentrations and the frequencies of splenic Tfh cells in B6.lpr mice. (E) Correlations of the frequencies of splenic Tfh cells with serum IgG and serum anti-dsDNA levels in B6.lpr mice. (F) B cells isolated from 6- to 8-week-old female B6 mice were cocultured with Tfh cells isolated from either B6.lpr mice (n = 5) or B6 mice (n = 5) for 5 days, and then the concentrations of IgG in the supernatants were detected. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. FSC, forward-scattered light; SSC, side-scattered light. Data were pooled from two independent experiments.
