Figure 5.
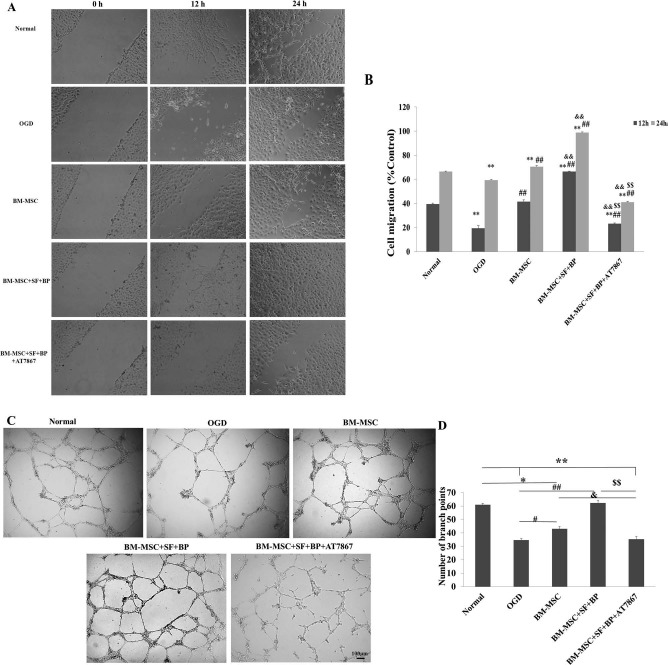
Wound healing and tube formation assay of HUVECs. (A, B) Cultured HUVECs were wounded using multichannel straight scratch with a pipette tip and treated with different conditional media for 24 h. The images of wound closure were taken, and a percentage of mean wound width of each treatment group was compared to control. It showed that the BM-MSC + SF + BP group significantly promoted HUVEC migration into denuded areas. (C, D) Cultured HUVECs on Matrigel-coated 96-well plates incubated with different conditional media for 24 h. Representative images of HUVEC tube formation were presented, and branch points in each group were counted to quantify endothelial tube formation. It indicated that BM-MSC + SF + BP group obviously enhanced the number of branch points compared to other groups. Data are expressed as means ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, versus Normal; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, versus OGD; &p < 0.05, & & p < 0.01, versus BM-MSC; $$p < 0.01, versus BM-MSC + SF + BP. HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; OGD, oxygen and glucose deprived; SD, standard deviation; SF, sodium ferulate; BP, n-butylidenephthalide; BM-MSC, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cell.
