Fig. 8.
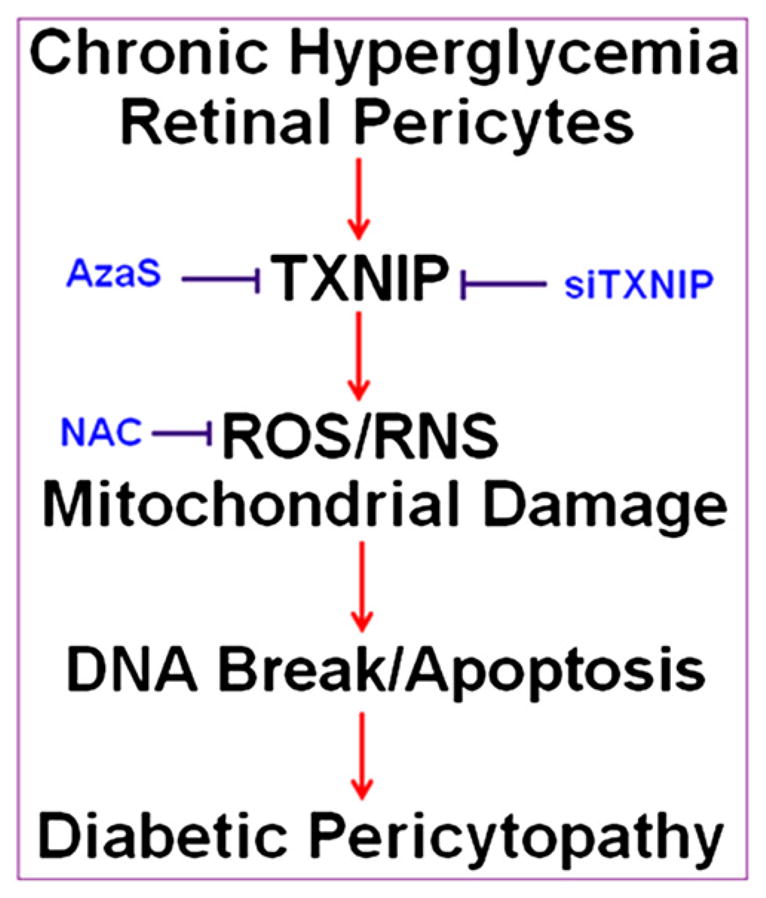
Summary: A potential role of TXNIP in hyperglycemia-induced ROS/RNS stress, DNA damage and pericyte demise (Pericytopathy) in DR. Chronic hyperglycemia-induced TXNIP up-regulation leads to cellular ROS/RNS stress, mitochondrial membrane depolarization, bioenergetic imbalance (low ATP), chromatin (DNA) fragmentation and pericyte apoptosis. Retinal pericytes appear to have a weaker anti-oxidant and mitophagic response to cellular stress to scavenge ROS and remove depolarized mitochondria, which leak ROS and are inefficient in ATP production. In addition, the DNA damage repair mechanism (p53 activation) is not evoked that may result in chromatin breakage and early demise of pericytes in DR. Anti-oxidant treatment such as NAC and a blockade of TXNIP via an inhibition of the HBP may represent potential therapeutic approaches to ameliorate DR pathogenesis.
