Fig. 2.
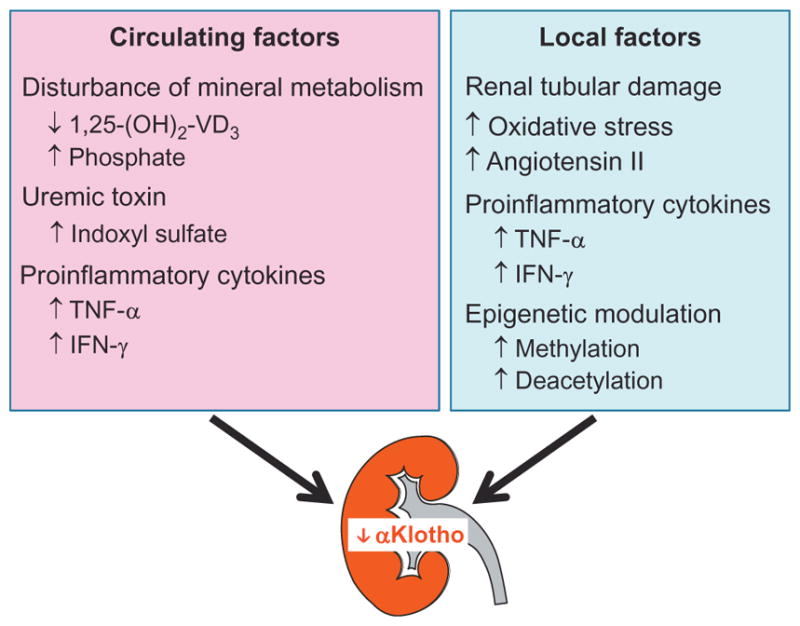
Circulating and local renal factors involved in the reduction of αKlotho expression in the kidney. In acute and chronic kidney disease, a variety of circulating factors including disturbed mineral metabolism, and accumulation of indoxyl sulfate and proinflammatory cytokines (left panel), can downregulate renal αKlotho expression. On the other hand, the elevation of reactive oxygen species, Ang II, and inflammatory cytokines in the diseased kidney can also downregulate renal αKlotho expression (right panel). Epigenetic modulation of αKlotho promoter via hypermethylation and deacetylation can reduce αKlotho expression and contribute to αKlotho deficiency in chronic kidney disease.
