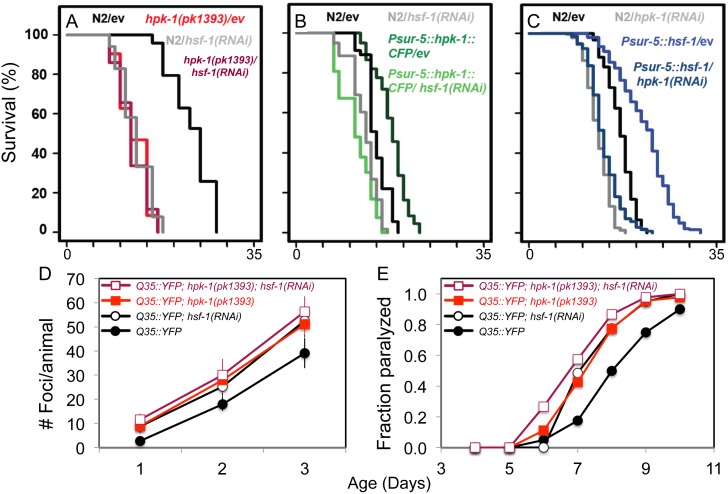
Fig 3. hpk-1 and hsf-1 have overlapping functions in longevity control and the preservation of proteostasis.
(A) hpk-1(pk1393) null mutant animals are short-lived compared to wild-type controls (red versus black) and hsf-1(RNAi) does not further shorten hpk-1(pk1393) lifespan (maroon versus gray). (B) Overexpression of hpk-1 increases lifespan (dark green versus black) and is hsf-1 dependent (light green). (C) Constitutive hsf-1 overexpression increases lifespan (blue versus black) and is hpk-1 dependent (light blue). Each graph is representative of at least 3 independent lifespan experiments. Full lifespan data can be found in S1 Table. (D-E) Simultaneous loss of hpk-1 and hsf-1 does not produce additive detrimental effects on protein homeostasis (maroon versus red). (D) Time course of Punc-54::Q35::YFP foci accumulation in conjunction with: treatment with control RNAi (filled circles/squares), hsf-1 RNAi (white circles/squares) in either wild-type (black traces) or the hpk-1(pk1393) null mutant background (colored traces). Data are the mean +/- S.D. of at least 15 animals from one representative trial; at least 5 independent experiments were performed. P-values are provided in Results and S3 Table. (E) Time course of paralysis of Punc-54::polyQ::YFP animals after treatment with control RNAi (filled circles/squares) or hsf-1 RNAi (white circles/squares) in either wild-type (black traces) or the hpk-1(pk1393) null mutant background (colored traces). Data is representative of one biological replicate, with at least 5 independent replicates performed. P-values and data from all trials are provided in S3 Table.