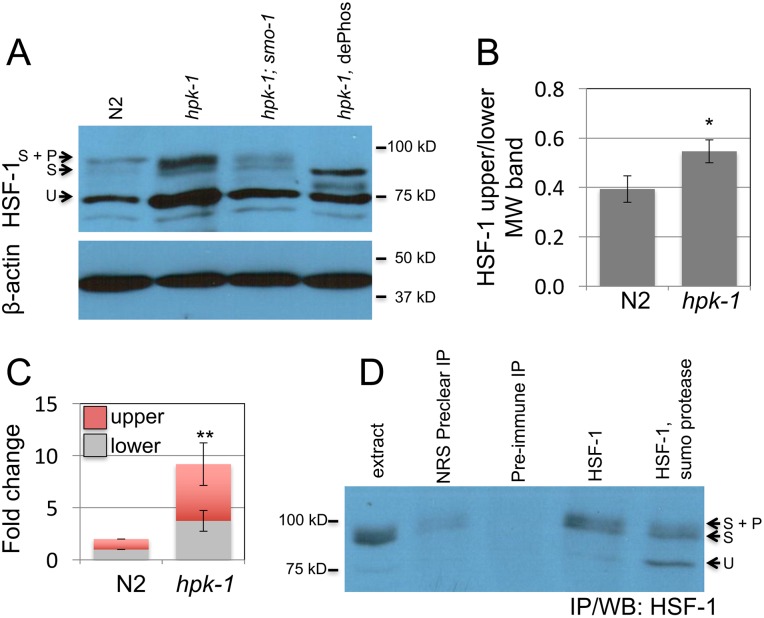
Fig 6. hpk-1 prevents sumoylation of HSF-1.
(A) Changes in HSF-1 post-translational modifications between early L4 wild-type and hpk-1(pk1393) animals were examined by western blot to HSF-1; smo-1(RNAi), which targets C. elegans SUMO, was used to block sumoylation, dePhos is lambda protein phosphatase treatment (other samples were mock treated). Beta-actin serves as a loading control. The ratio of modified to unmodified HSF-1 is 0.35, 0.51, and 0.35 for N2/ev, hpk-1(pk1393)/ev, and hpk-1(pk1393)/smo-1(RNAi), respectively (see S3A Fig for additional data). (B) hpk-1 prevents sumoylation of HSF-1. Ratio of HSF-1 unmodified (75kD) to modified (90-95kD, sumoylated and sumoylated plus phosphorylated). The S.E.M. from Image J quantification is shown for seven N2 and hpk-1(pk1393) replicates (* p<0.02, Student’s t-test, see S3B and S3C Fig for additional data). (C) Loss of hpk-1 induces HSF-1 in L4 animals. Protein levels of unmodified (75kD, grey), modified (90-95kD, red) HSF-1, and beta-actin were quantified in ImageJ for four replicates (see S3C Fig for additional data). (For total, upper, and lower MW fold change (respectively): ** p<0.01, <0.01, and <0.02, Student’s t-test). (D) Immunoprecipitation of HSF-1 from hpk-1(pk1393) animals followed by SUMO protease or mock treatment. First lane is protein extract prior to immunoprecipitation. Lysate was precleared of nonspecific interactions by treatment with normal rabbit serum (Invitrogen #01–6101) that was then immunoprecipitated (lane 2). Precleared lysate was then evenly divided and treated with either preimmunized rabbit serum (i.e. serum from the rabbit in which C. elegans HSF-1 antibodies were generated, prior to immunization, lane 3) or HSF-1 antiserum, followed by immunoprecipitation. Immunoprecipitated HSF-1 was then either mock treated or treated with SUMO protease (lanes 4 and 5). See methods for additional details.