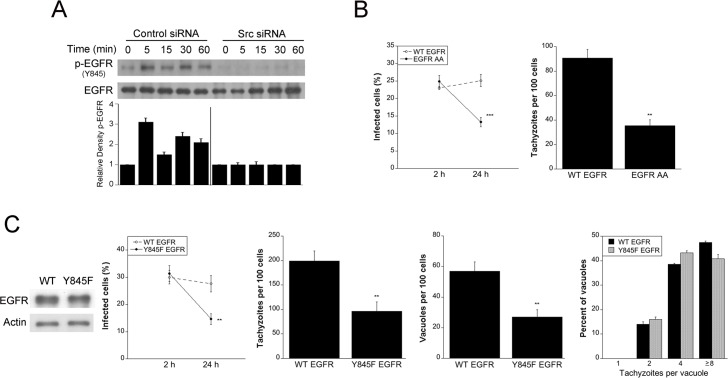
Fig 5. Src signaling induced by T. gondii triggers trans-activation of EGFR that is required to prevent parasite killing within host cells.
A, A549 cells were transfected with control siRNA or Src siRNA followed by challenge with RH T. gondii. Expression of total EGFR and phospho-Y845 EGFR was assessed by immunoblot. A vertical line was inserted between densitometry data of lysates from cells transfected with control or Src siRNA to indicate that relative densities of phospho-Y845 EGFR from infected cells were compared to bands from their respective uninfected (control) cells. Relative density of phospho-Y845 EGFR for uninfected samples was given a value of 1. Densitometry data represent means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. B, NMuMG with stable expression of WT EGFR or EGFR AA mutant were challenged with RH T. gondii. Monolayers were examined at 2 and 24 h to determine the percentages of infected cells and at 24 h to ascertain the numbers of T. gondii tachyzoites per 100 cells. C, A549 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding WT EGFR or Y845F EGFR followed by challenge with RH T. gondii. Monolayers were examined at 2 and 24 h to determine the percentages of infected cells, and at 24 h to ascertain the numbers of T. gondii tachyzoites, T. gondii-containing vacuoles per 100 cells and parasites per vacuole. Results are shown as the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.