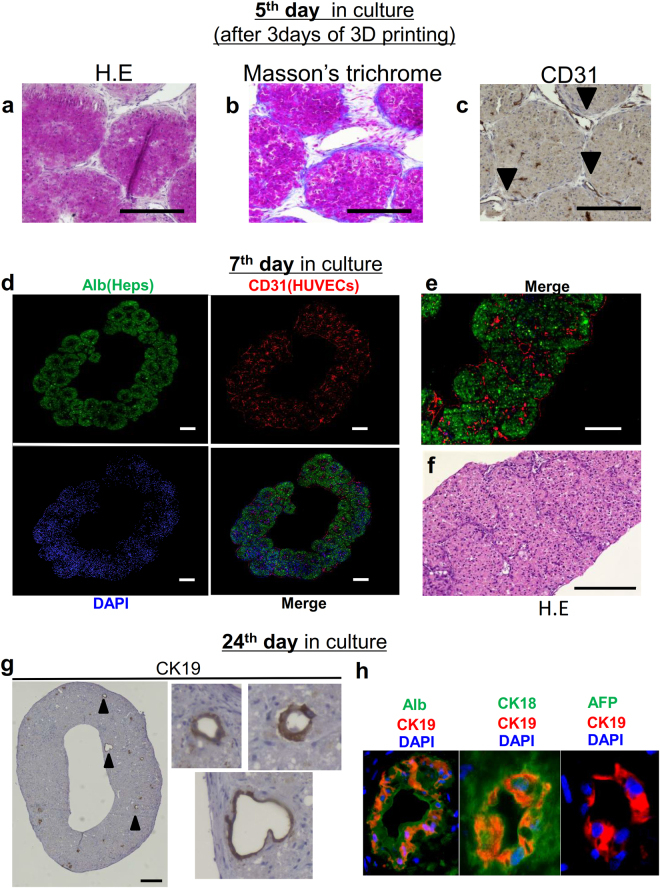
Figure 7.
The histological analysis of ex vivo-fabricated liver-like tissue. (a,b,c) The histological analysis of the structures on the needles (3days after 3D printing) by hematoxylin-eosin staining, Masson’s trichrome staining and immunostaining using anti-human CD31 antibodies. (b) During tissue construction, the cells self-produced ECM. (c) HUVECs (indicated by the arrowheads) covered the surface of the tissue. (d,e) Fluorescence images of the liver-like tissue on the 7th day in culture. hHeps were stained with anti-human albumin antibodies (green) and HUVECs were stained with anti-human CD31 antibodies (red). The production of albumin by hHeps and the formation of reticular endothelial networks inside the liver-like tissue were verified. Scale bars, 200 μm. (f) An HE-stained cross-section on the 7th day in culture. The hepatocytes were viable, even in the center of the tissue, the thickness of which was approximately 600 μm. Scale bars, 100 μm. (g) Immunostaining of the liver-like tissue on the 24th day in culture. CK19-positive cells and a duct-like morphology were observed. The arrowheads indicate the CK19-positive cells with a duct-like morphology. Scale bars, 200 μm. (h) Fluorescence images of the bile duct-like structure in the liver-like tissue.