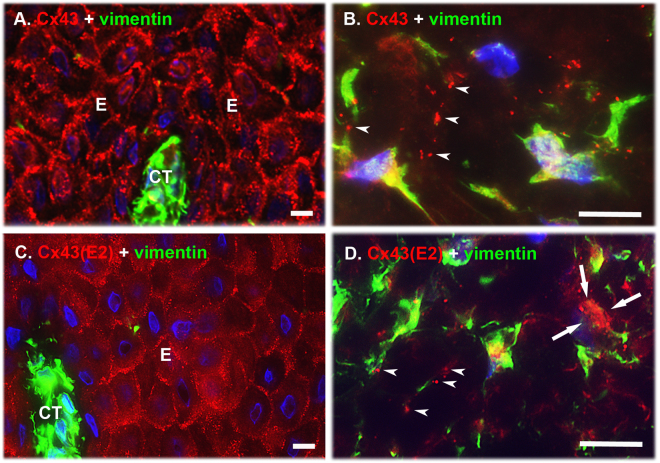
Figure 1.
Localization of Cx43 GJs and HCs in human gingiva in vivo. Representative images of human gingival tissue sections double immunostained with an antibody recognizing all forms of the Cx43 molecule (Cx43; A and B) or only HC-associated Cx43 (Cx43(E2); C and D) and vimentin (a mesenchymal cell marker) in human gingival epithelium (A and C) and connective tissue (B and D). In the basal and spinous layers of the epithelium, Cx43 immunostaining localized most abundantly at the cell-cell contacts as fairly large plaque-like structures typical to GJs (A). Staining with the Cx43 HC-specific Cx43(E2) antibody also showed localization of Cx43 at the epithelial cell-cell contacts, but the immunopositive structures were markedly smaller. In addition, some punctate immunoreactivity was noted on the cell body of the keratinocytes (C). (B) In the gingival connective tissue, Cx43 immunoreactivity was also present as large plaque-like staining that mostly localized in the long cellular processes reaching out from the vimentin-positive cells (arrowheads). (D) In these cells, Cx43 HCs detected by the Cx43(E2) antibody were also mainly present as plaque-like structures that localized in the cell processes (arrowheads), but some staining was also present on the cell body (arrows). Representative immunostaining images from a minimum of three parallel sections from three individual donors are shown. Nuclear staining (blue) was performed using DAPI. E: Epithelium; CT: Connective tissue. Magnification bars = 10 μm.