Figure 6.
LC-MS/MS Reveals Highly Selective OTULIN Coupling and E1-Dependent Auto-Conjugation of OTULIN ABP
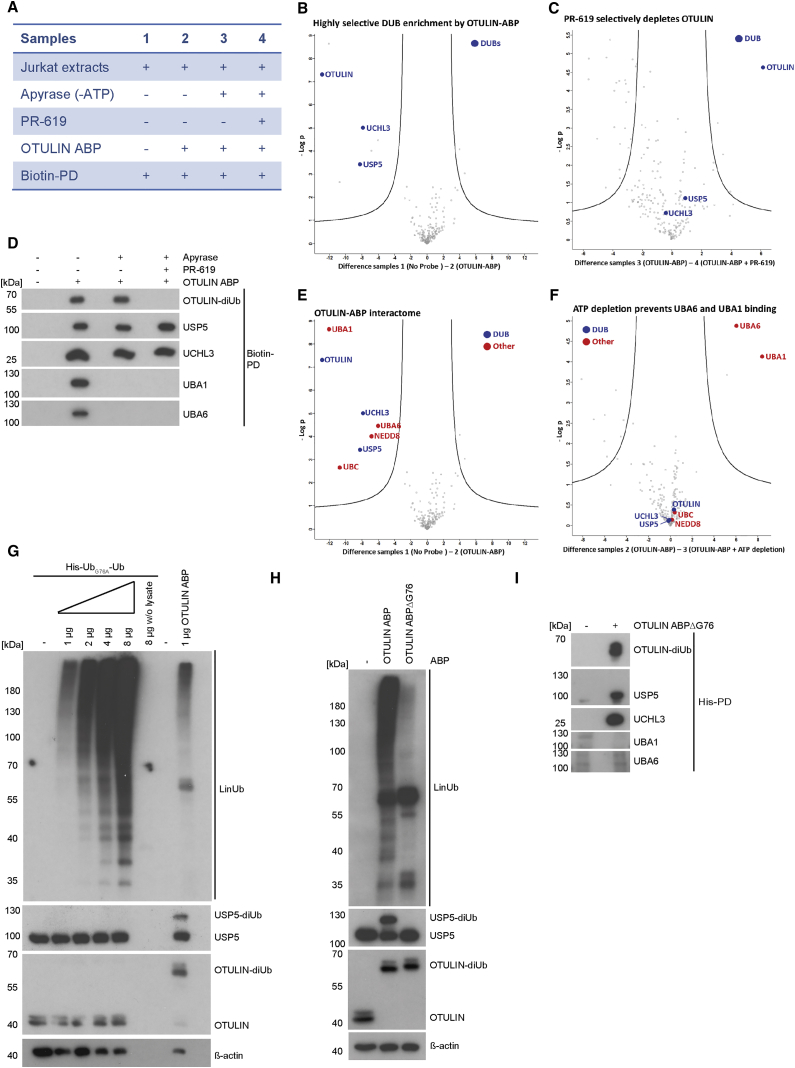
(A) Overview of ABP-PD samples analyzed by LC-MS/MS.
(B) Volcano plot demonstrating enrichment of identified DUBs (blue) after biotin-PD in the presence (sample 2) compared with the absence (sample 1) of OTULIN ABP. Curves depict significant enrichment or depletion, respectively. See also Table S2.
(C) Volcano plot demonstrating loss of DUB binding (blue) between control (sample 3) and PR-619 (sample 4) treatments before OTULIN ABP incubation and biotin-PD. Curves depict significant enrichment or depletion, respectively.
(D) Biotin-PDs from extracts of Jurkat T cells (2 × 107) were performed using the same conditions as for LC-MS/MS analyses and analyzed by western blot.
(E) Volcano plot demonstrating selective binding of DUBs (blue) and other proteins (red) to OTULIN ABP (sample 1 versus 2). Curves depict significant enrichment or depletion, respectively.
(F) Volcano plot demonstrating loss of UBA1 and UBA6 binding to OTULIN ABP upon ATP depletion (sample 2 versus 3). Curves depict significant enrichment or depletion, respectively.
(G) Extracts of HEK293 cells (6 × 105 cells) were incubated with increasing amounts of His-UbG76A-Ub or with 1 μg OTULIN ABP (45 min, 30°C). Ubiquitin chain formation and OTULIN-diUb or USP5-diUb complexes were analyzed by western blot using anti-M1-polyUb and DUB-specific antibodies.
(H) Extracts of HEK293 cells (6 × 105 cells) were incubated with 1 μg OTULIN ABP or 1 μg OTULIN ABPΔG76 (45 min, 30°C). Labeling of OTULIN and USP5 as well as Ub chain formation was analyzed by western blot.
(I) Extracts of Jurkat T cells (2 × 107 cells) were treated with OTULIN ABPΔG76 before His-PD. Interactions between the new probe and the indicated proteins were analyzed by western blot.