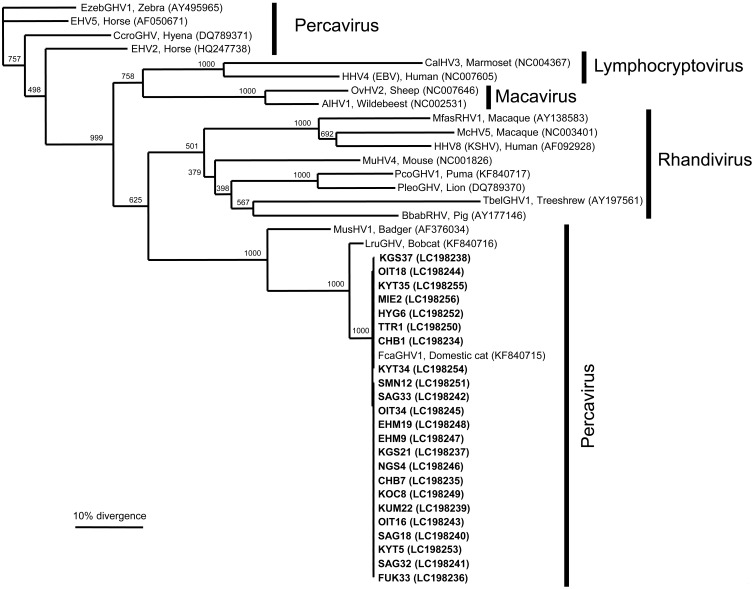
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic relationships of various gammaherpesviruses based on the nucleotide sequences of the glycoprotein B gene. Scale bar indicates the genetic distance (0.1 substitutions/site). The 23 clones of FcaGHV1 detected in this study are shown in bold (LC198234–LC198256). Pathogen names, host species, and GenBank accession numbers (in parentheses) of the sequences are shown on the phylogenetic tree: Human herpesvirus 4 (HHV4, Epstein-Barr virus, NC007605); Callitrichine herpesvirus 3 (CalHV3, NC004367); Alcelaphine herpesvirus 1 (AlHV1, NC002531); Ovine herpesvirus 2 (OvHV2, NC007646); Mustelid herpesvirus 1 (MusHV1, AF376034); Felis catus gammaherpesvirus 1 (FcaGHV1, KF840715); Lynx rufus gammaherpesvirus 1 (LruGHV1, KF840716); Equid herpesvirus 2 (EHV2, HQ247738); Equid herpesvirus 5 (EHV5, AF050671); Crocuta crocuta gammaherpesvirus 1 (CcroGHV1, DQ789371); Equus zebra gammaherpesvirus 1 (EzebGHV1, AY495965); Tupaia belangeri gammaherpesvirus 1 (TbelGHV1, AY197561); Macacine herpesvirus 5 (McHV5, NC003401); Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8, Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, NC009333); Macaca fascicularis rhadinovirus 1 (MfasRHV1, AY138583); Murid herpesvirus 4 (MuHV4, NC001826); Puma concolor gammaherpesvirus 1 (PcoGHV1, KF840717); Panthera leo gammaherpesvirus 1 (PleoGHV1, DQ789370); and Babyrousa babyrussa rhadinovirus 1 (BbabRHV1, AY177146). The number under each internal nodes indicates the percentage of 1,000 bootstrap replicates that supported the branch.