Figure 3.
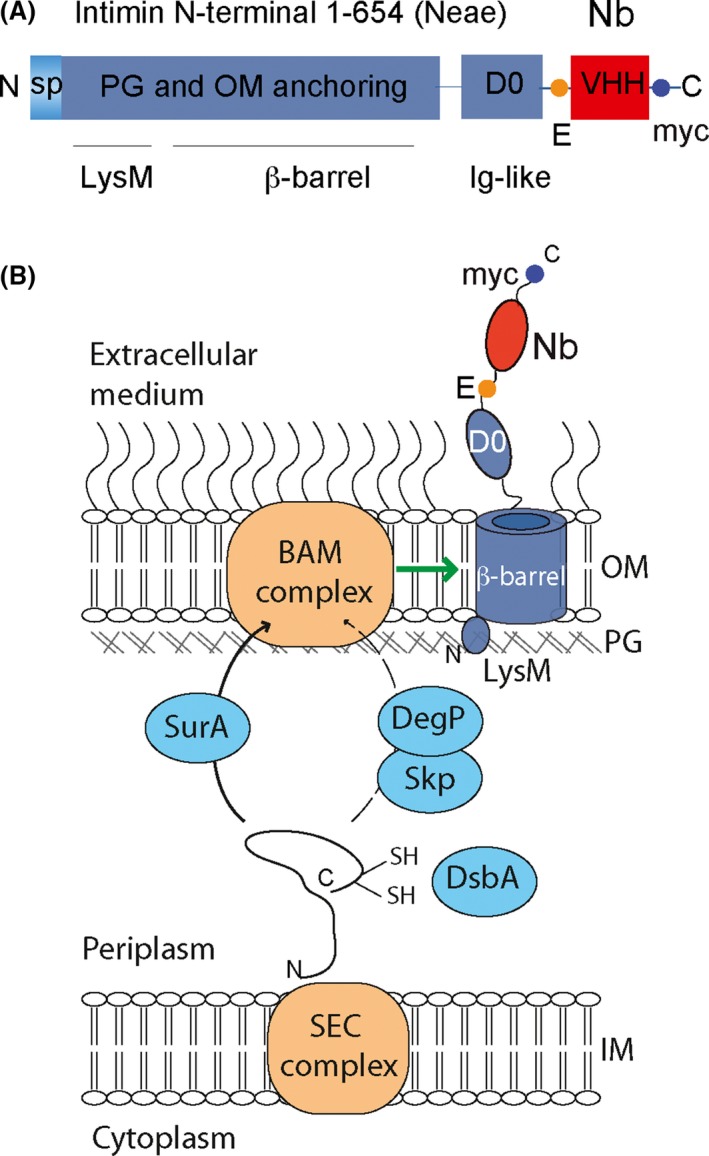
Structure of Neae‐VHH fusions and their secretion mechanism in E. coli display of nanobodies. (A) Linear representation of the polypeptide encoded by Neae‐VHH fusions for E. coli display. The intimin fragment Neae (residues 1–654) comprises the N‐terminal signal peptide (sp), LysM domain for PG binding, β‐barrel for OM‐anchoring and exposed D0 Ig‐like domain. The VHH encodes the Nb. The Neae‐VHH fusion also contains the E‐tag and myc‐tag epitopes flanking the VHH. (B) The fusion polypeptide expressed in the bacterial cytoplasm is translocated across the IM via the Sec complex. In the periplasm, chaperones assist folding of the Nb and transport of the intimin β‐barrel domain to the BAM complex in the OM. The BAM complex is responsible for the folding and insertion of the intimin β‐barrel in the OM and participates in the translocation of the D0 and Nb domains to the bacterial surface. The epitopes E‐ and myc‐tags are used for the immunodetection of Nb displayed on E. coli surface by flow cytometry.
