Figure 4.
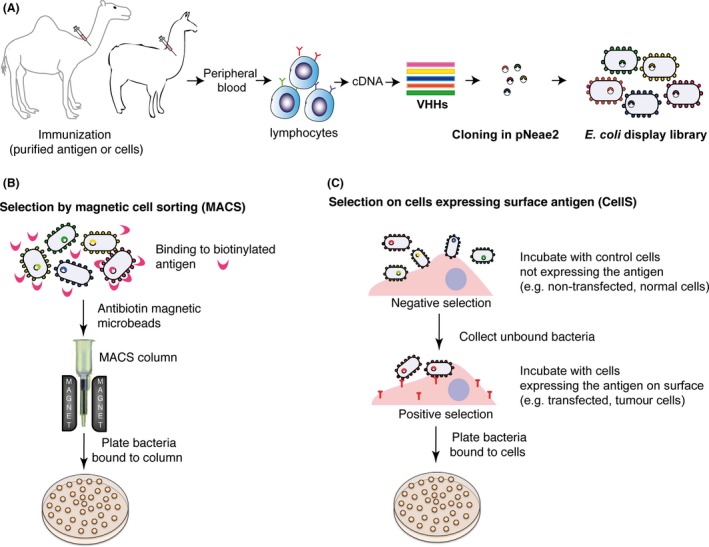
Generation of E. coli display immune libraries and their selection by magnetic cell sorting (MACS) and on mammalian cells (CellS). (A) Scheme of the generation of an E. coli display immune library of Nbs. Animals (e.g. dromedaries or llamas) are immunized with either purified antigen or cells expressing the target antigen. After immunization, the VHH gene segments are amplified from peripheral blood lymphocytes by RT‐PCR, cloned into plasmid vector pNeae2 and induced on E. coli for surface display. (B) Selection of an E. coli display library using MACS. Escherichia coli bacteria are incubated with the biotinylated antigen and antibiotin magnetic beads. Bacteria with bound antigen are captured in an iron column held in a magnet. Elution of bound bacteria is carried out with fresh LB media upon column removal from the magnet and grown by plating. (C) Selection of an E. coli display library on mammalian cells (CellS). Escherichia coli bacteria are initially incubated with control cells lacking expression of the target antigen (negative selection). Bacteria that do not bind to control cells are incubated with cells expressing the target antigen on their surface for positive selection. Bacteria bound to antigen‐positive cells after washing (e.g. PBS) are recovered by lysis of the mammalian cells and grown by plating.
