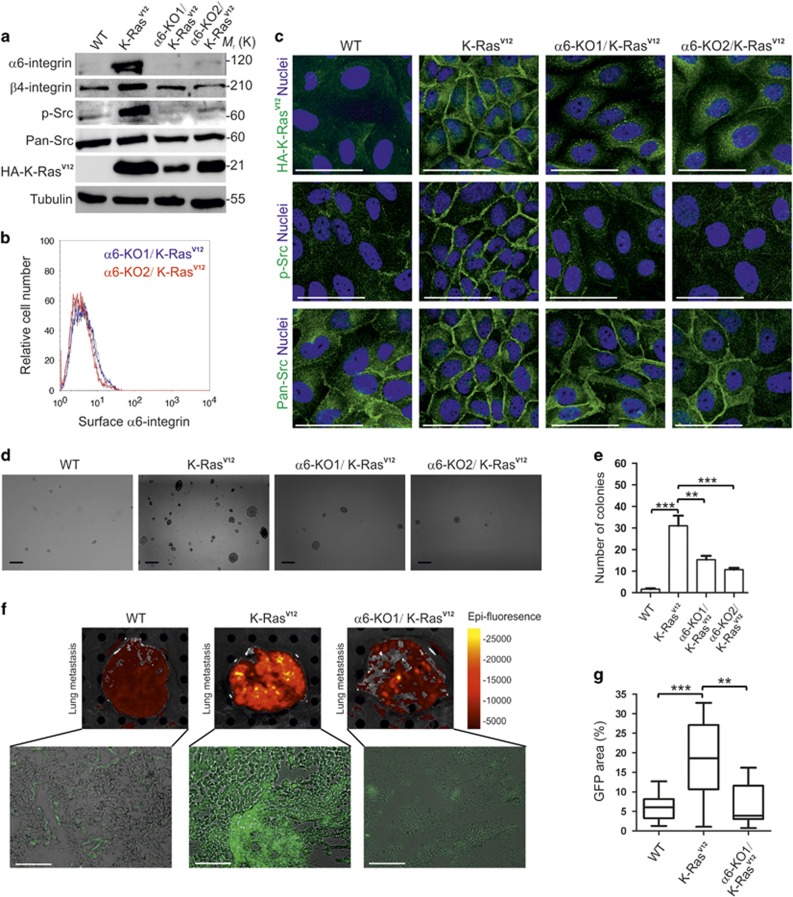
Figure 3.
α6-integrin is required for K-RasV12-induced anoikis resistance. (a) Western blot analysis of WT, K-RasV12 and two independent α6-KO/K-RasV12-MDCK cell line lysates using antibodies against α6-integrin, β4-integrin, phosphorylated-Src (pTyr416; p-Src), pan-Src, Hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged K-RasV12 (HA-K-RasV12) and tubulin. (b) FACS analysis of surface expressed α6-integrin in WT (left panel; blue) and K-RasV12 (left panel; red) MDCK cells or α6-KO1/K-RasV12 (right panel; blue) and α6-KO2/K-RasV12 (right panel; red). Unlabeled cells (only secondary antibody) are shown in gray. (c) Confocal sections of WT-, K-RasV12- and α6-KO/K-RasV12-MDCK cells stained for K-RasV12 (HA-K-RasV12), Tyr416-phosphorylated-Src (p-Src) and total Src (pan-Src). Nuclei were visualized by 2-(4-amidinophenyl)-1H -indole-6-carboxamidine (DAPI). Scale bars=100 μm. (d) WT-, K-RasV12, α6-KO1/K-RasV12 and α6-KO2/K-RasV12-MDCK cells were grown in soft agar and colony formation efficiency was determined as previous described.68 Scale bars=100 μm. (e) Quantification of colony formation in WT, K-RasV12, α6-KO1/K-RasV12 and α6-KO2/K-RasV12 MDCK cells cultured in soft agar for 15 days. (f) Representative images of whole lungs from mice injected with GFP-expressing WT-, K-RasV12 and α6-KO1/K-RasV12-MDCK cells using IVIS Spectrum imaging system (upper panel). Representative fluorescence microscopy images of cryosections from lungs (lower panels). Scale bars=100 μm. (g) Quantification of lung metastases as area of GFP-positive colonies relative to the total lung tissue area. Data are presented as the mean±s.d. At least 10 randomly selected slides were analyzed per each sample. Statistical significance was determined using two-tailed t-test. *P-values<0.05, **P-values<0.01 and ***P-values<0.001.