FIGURE 10.
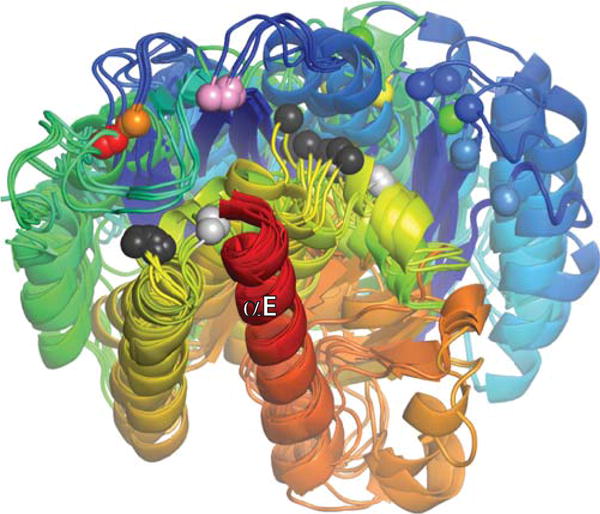
Superposition of all currently published serine resolvase catalytic domain structures, aligned using their E helices as guides. Each structure is shaded from blue (N-ter) to red (end of catalytic domain), and all unique copies from the asymmetric unit for each structure were used (two to four per structure). Colored spheres mark the positions of the active site serines. From right to left (roughly), they are: light blue, wild-type (WT) Sin from the Sin–site II structure (PDBid 2r0q); dark blue, WT γδ determined without DNA (PDBid 2rsl); green, WT γδ from the γδ–site I complex structure (PDBid 1gdt); yellow, activated γδ from a structure without DNA (PDBid 2gm5); orange and red, two different activated variants of γδ from structures with covalently linked crossover site DNA (PDBids 1zr4 and 2gm4, respectively), and pink, activated Sin tetramer (determined without DNA; PDBid 1pkz). Black and Gray spheres mark the Cα positions of the probable general acid R71 (γδ)/R69 (Sin). Those that cluster towards the left are in structures of activated mutants, whereas those that cluster towards the right are from WT structures. doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.MDNA3-0045-2014.f10
