FIGURE 4.
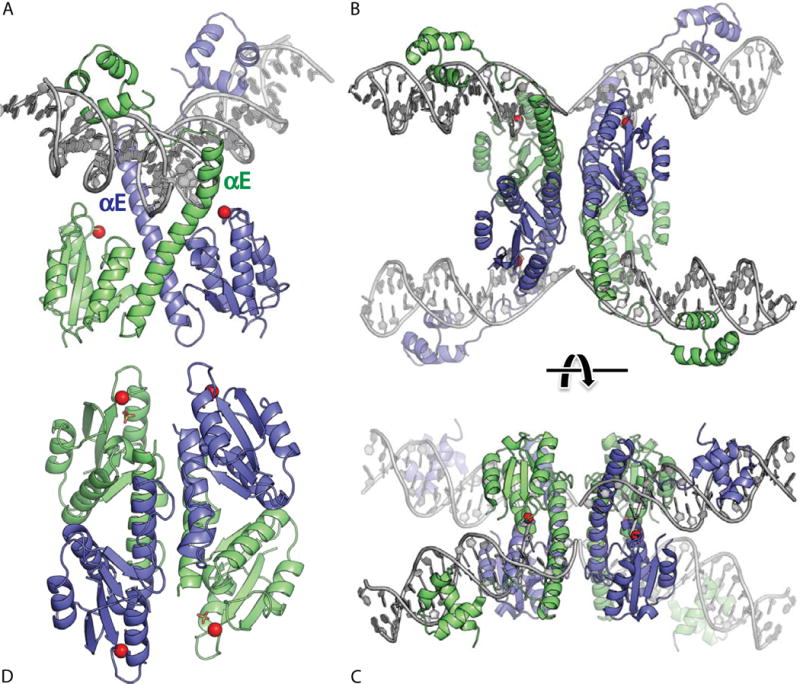
Serine resolvase structures. (A) Wild-type γδ resolvase bound to crossover site (or “site I”) DNA. The active site serine residues are marked with red spheres (PDBid 1gdt; (31)). (B) Activated mutant γδ resolvase with crossover site DNA in the covalent protein–DNA intermediate state. Note that each catalytic domain has undergone major conformational changes in the transition from dimer to tetramer (PDBid 2gm4; (48, 49)). (C) The same structure as in B, rotated by ∼90° about a horizontal axis. (D) Activated Sin resolvase tetramer catalytic domain tetramer. Sulfate ions that mark the binding pockets for the scissile phosphate are shown as sticks (PDBid 3pkz) (50). doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.MDNA3-0045-2014.f4
