Figure 3. The RAB11a effector RAB11FIP3 and Dynein are involved in bacterial expulsion.
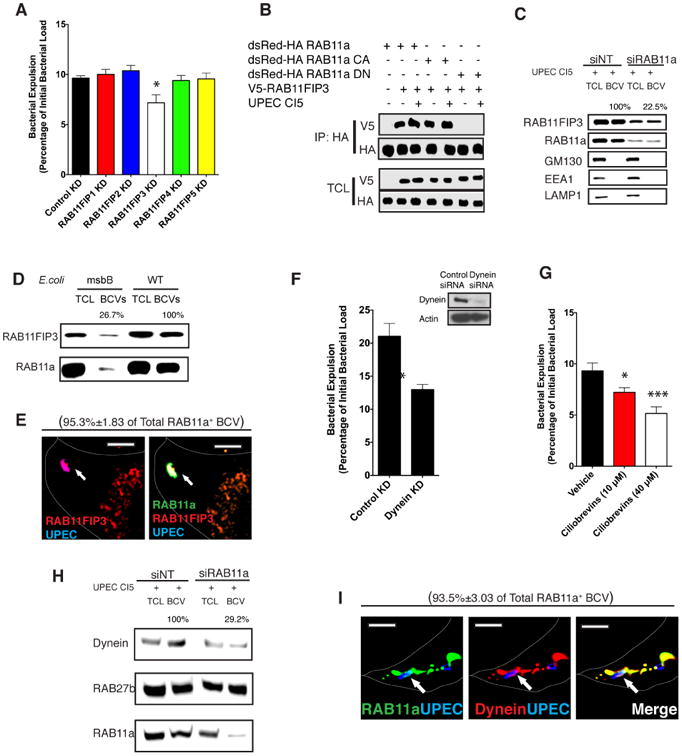
(A) Bacterial expulsion from infected BECs transfected with control siRNA or siRNA targeting RAB11FIP1, RAB11FIP2, RAB11FIP3, RAB11FIP4 orRAB11FIP5 respectively. Error bars represent SEM. The experiments were repeated three times, where each experiment employed n=6 wells.
(B) HA tagged WT RAB11a and constitutively active (CA) or dominant negative (DN) mutants of RAB11a were immunoprecipitated from naïve or infected BECs. The association between RAB11a and RAB11FIP3 in different conditions was examined by western blotting of the IP fractions. The protein of interests in the total cell lysates (TCL) was also depicted to indicate that similar levels of RAB11 or RAB11FIP3 protein was present in each fraction.
(C) Immunoblots of RAB11FIP3 in total cell lysates (TCL) or bacteria-containing vesicle (BCV) fractions isolated from infected BECs which were pre-transfected with control siRNA or siRNA targeting RAB11a. Unrelated organelle markers (GM130 for Golgi, EEA1 for early endosome, LAMP1 for late endosome and lysosome) were employed to demonstrate the purity of BCV isolation.
(D) Protein immunoblots of RAB11FIP3 and RAB11a in total cell lysate (TCL) or bacteria-containing vesicle (BCV) fractions isolated from BECs infected with WT or msbB mutant E.coli which cannot activate TLR4 signaling. Unrelated organelle markers (GM130 for Golgi, EEA1 for early endosome, LAMP1 for late endosome and lysosome) were used to demonstrate the purity of BCV isolation.
(E) Immunofluorescence staining of infected BECs revealing the co-association of RAB11a (green) and RAB11FIP3 (red) with UPEC (blue). Scale bar: 5 μm.
(F) Bacterial expulsion from infected BECs transfected with control siRNA or siRNA targeting the light chain of Dynein. Error bars represent SEM. The experiments were repeated three times, where each experiment employed n=6 wells.
(G) Bacterial expulsion from infected BECs treated with vehicle control or a specific inhibitor of Dynein. Error bars represent SEM. The experiments were repeated three times, where each experiment employed n=6 wells.
(H) Immunoblots of Dynein in total cell lysates (TCL) or bacteria-containing vesicle (BCV) fractions isolated from infected BECs which are pre-transfected with control siRNA or siRNA targeting RAB11a.
(I) Immunofluorescence staining of infected BECs revealing the co-association of RAB11a (green) and Dynein (red) with UPEC (blue). Scale bar: 5 μm. See also Figure S2
