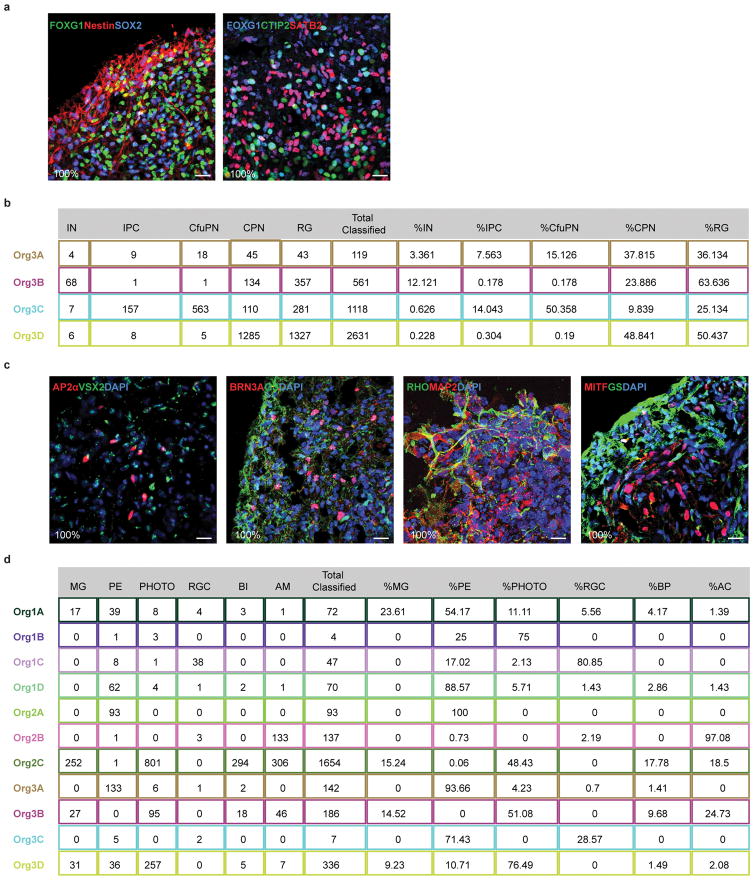
Extended Data Figure 4. Distribution and reproducibility of forebrain and retina cell types across organoids.
a. Immunohistochemical detection in a 6 month old organoid of the forebrain marker FOXG1 with the progenitor markers Nestin and SOX2 (left) and of FOXG1 with the corticofugal projection neuron marker CTIP2 and the callosal projection neuron marker SATB2 (right), all showing extensive co-coexpression, which was observed in all organoids examined (6 of 6). b. Count of cells assigned to each cortical cell type in individual organoids from Flask 3, and the percentage of each cell type out of all classified cortical cells in that organoid. c. Immunohistochemical detection of retinal cell types in 6 month organoids shows expression of known markers for amacrine cells, bipolar cells, retinal ganglion cells, Muller glia, rods, and retinal pigmented epithelium, observed across all organoids in every flask, n=11, 3 bioreactors. d. Count of cells assigned to each retinal cell type in individual organoids from Flasks 1, 2, and 3, and the percentage of each cell type out of all classified retinal cells in that organoid. IN: interneurons; IPC: intermediate progenitor cells; CfuPN: corticofugal projection neurons; CPN: callosal projection neurons; RG: radial glial cells; MG: Muller glia; PE: pigmented epithelium; PHOTO: photoreceptors; RGC: retinal ganglion cells; BP: bipolar cells; AC: amacrine cells.