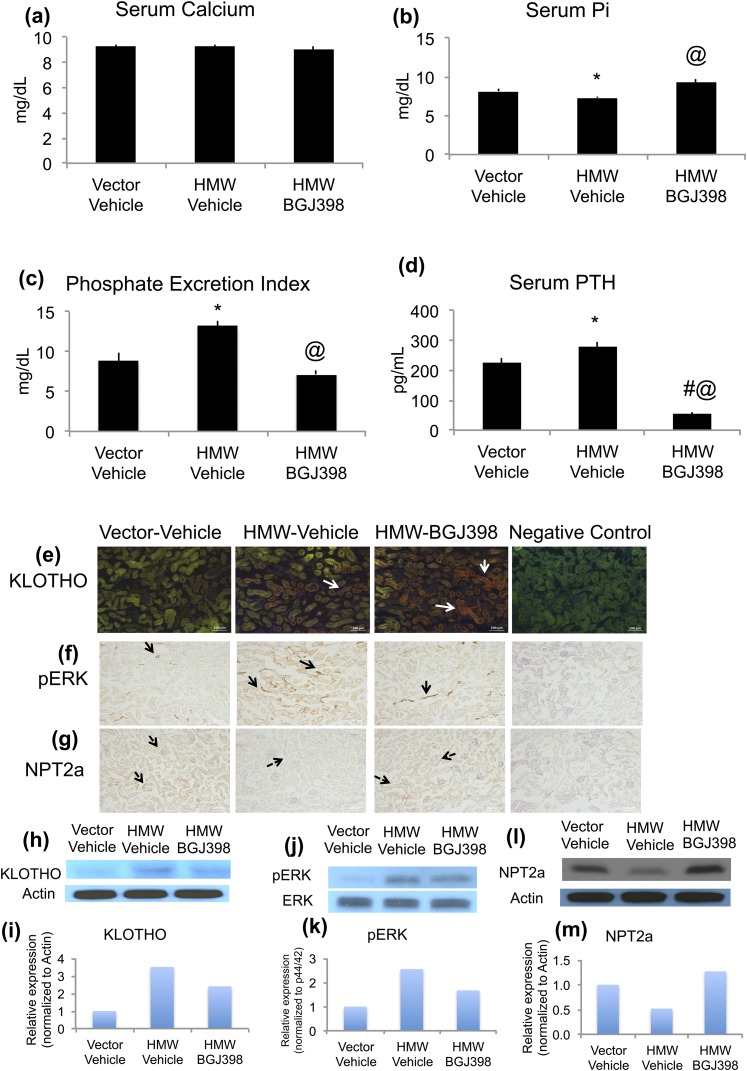
Figure 2.
Effects of long-term NVP-BGJ398 treatment on mineral ion homeostasis and FGF23-KLOTHO axis in kidney in HMWTg mice. Starting at 5 weeks of age, HMWTg mice were treated with the FGFR inhibitor NVP-BGJ398 (50 mg/kg, oral) or vehicle three times per week for 8 weeks. Vector mice were treated with vehicle only. Mice were euthanized 24 hours after the last NVP-BGJ398 administration. Serum and kidneys were collected during euthanasia. (a) Serum calcium was measured, n = 8 to 15 per group; (b) serum Pi was measured, n = 8 to 14 per group. (c) PEI was determined, n = 5 to 8 per group; (d) serum PTH was determined, n = 4 to 6. Data are mean ± SE. *Vector-Vehicle vs HMWTg-Vehicle, P < 0.05; #Vector-Vehicle vs HMWTg- NVP-BGJ398, P < 0.05; @HMWTg-Vehicle vs HMWTg- NVP-BGJ398, P < 0.05. (e, h, i) Immunofluorescence staining and immunoblotting for detection of KLOTHO, (f, j, k) Pp44/42, and (g, l, m) NPT2a protein expression in mouse kidneys. Note increased KLOTHO and pERK and decreased NPT2a protein expression in HMW-Vehicle kidneys. NVP-BGJ398 treatment normalized pERK and NPT2a expression in HMWTg mice. Negative control had no primary antibody during immunostaining.