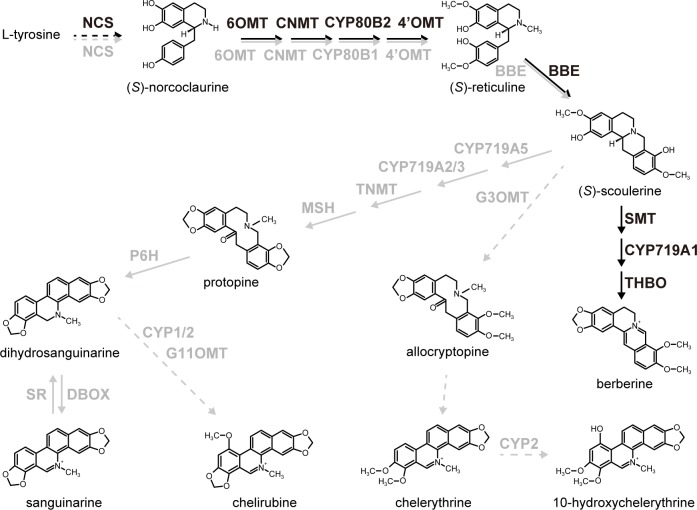
Fig 1. BIA biosynthetic pathways in BIA-producing plants.
Black and gray letters show biosynthetic enzymes in C. japonica and E. californica, respectively. Broken lines indicate uncharacterized enzyme reactions. NCS, (S)-norcoclaurine synthase; 6OMT, (S)-norcoclaurine 6-O-methyltransferase; CNMT, (S)-coclaurine-N-methyltransferase; CYP80B1, (S)-N-methylcoclaurine 3’-hydroxylase; 4’OMT, (S)-3’-hydroxy-N-methylcoclaurine 4’-O-methyltransferase; BBE, berberine bridge enzyme; SMT, (S)-scoulerine 9-O-methyltransferase of C. japonica; CYP719A1, (S)-canadine synthase; THBO, (S)-tetrahydroprotoberberine oxidase; CYP719A5, (S)-cheilanthifoline synthase; CYP719A2/3, (S)-stylopine synthase; TNMT, (S)-tetrahydroprotoberberine cis-N-methyltransferase, MSH, (S)-N-methylstylopine 14-hydroxylase; P6H, protopine 6-hydroxylase; DBOX, dihydrobenzophenanthridine oxidase; SR, sanguinarine reductase; G3OMT, (S)-scoulerine 9-O-methyltransferase of California poppy; G11OMT, putative 10-hydroxydihydrosanguinarine 10-O-methyltransferase. CYP1 and CYP2 are putative dihydrobenzophenanthridine 10-hydroxylases.