Fig. 3.
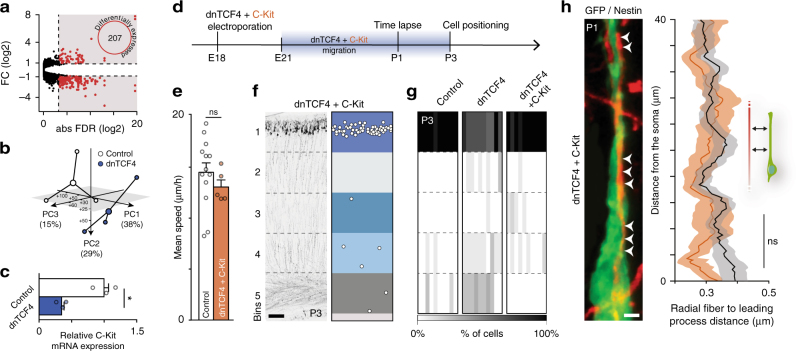
Wnt LOF perturbs leading process-radial fiber interactions via C-kit. a RNA sequencing identified 207 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between control and dnTCF electroporated migrating neurons (selection by fold change (FC) of > 0.9 and < −0.9 and false discovery rate (FDR) of ≤ 0.1). b Three independent experiments plotted by principal components (PC) from PC analysis based on DEGs in control and dnTCF4 migrating neurons. See also Supplementary Table 1. c Relative C-Kit mRNA expression quantified by qRT-PCR on sorted migrating cells at P0 from control and dnTCF4 electroporated brains; n = 3 experiments, Student’s t test. d Timeline of rescue experiments with transient dnTCF4 and C-Kit co-expression during migration. e C-Kit overexpression during migration restores locomotion speed; n = 13 and five brains (Control and dnTCF4 + C-Kit, respectively), Mann–Whitney, P = 0.1734. f C-Kit overexpression reduces the proportion of delayed neurons represented in coronal section from a dnTCF4 + C-Kit electroporated brain at P3. g Heatmap of P3 cortical cell distribution, color-coded columns represent n = 10 brains per condition. h Representative image illustrating migrating cells attached to nestin-positive radial glia fibers. C-Kit overexpression in migrating cells restores a normal adhesion to the radial glia (arrowheads). Point-by-point measurement of the distance between the leading process of migrating cells and the radial fiber; n = 50 cells per condition from 4 brains, two-way ANOVA, P = 0.1231. Graphs display mean ± s.e.m. ns, non-significant, *P < 0.05. Bar = 2 μm (h) and 100 μm (f)