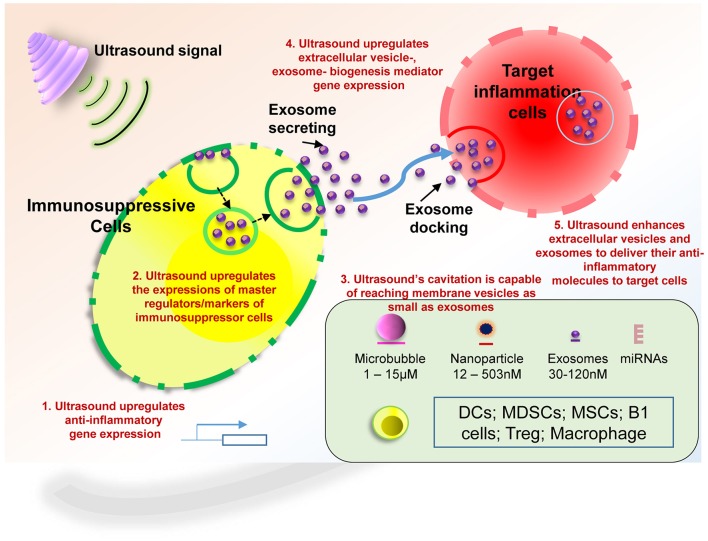
Figure 11.
Our novel working model which proposes the potential anti-inflammatory mechanisms utilized by LIUS to exert its beneficial effects. These potential mechanisms are as follows; (1) LIUS upregulates the expression of anti-inflammatory/immunosuppressive genes in the ultrasound-treated cells; (2) LIUS enhances the expression of the master regulators (markers) of immunosuppressor cells; (3) LIUS mediated cavitation is capable of reaching the membrane vesicles as small the expression of extracellular vesicles; and (4) LIUS increases exosome biogenesis and docking mediators, and (5) Ultrasound enhances extracellular vesicles and exosomes to deliver their anti-inflammatory molecules to target cells. Our new findings suggest that LIUS inhibits inflammation via above discussed novel mechanisms to make the target inflammatory cells become less inflammatory. DCs, dendritic cells; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; B1 cells, CD5+ B1 B cells; Treg, CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells.