Fig. 2.
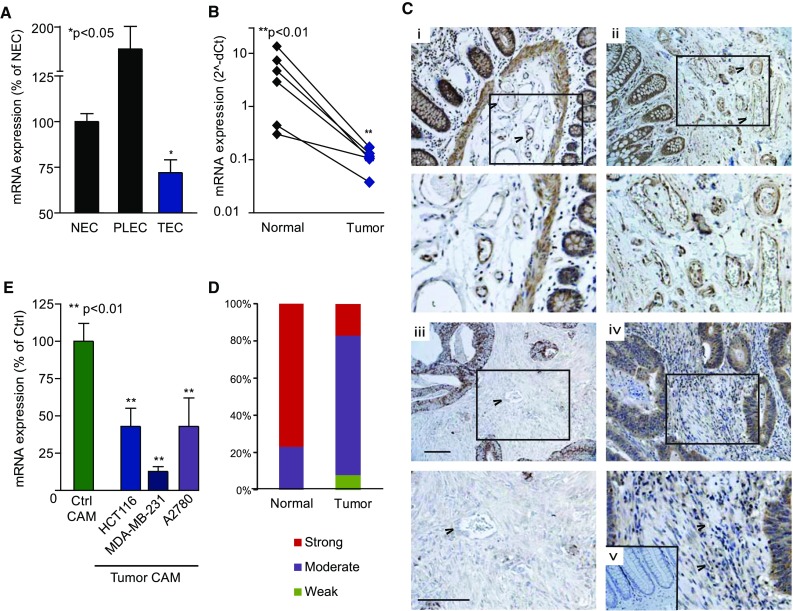
Expression of BRD7 is suppressed in tumor vasculature. a BRD7 expression is substantially reduced in tumor EC (TEC) as compared to normal EC (NEC) and placenta EC (PLEC) as shown by qPCR. *p < 0.05 Kruskal–Wallis test. b qPCR analysis of total tumor RNA confirms the global suppression of BRD7 in tumors. **p < 0.01 paired t test. c BRD7 protein is detected in EC and underlying structures (e.g., muscular layers) of blood vessels as well as in the crypts of normal colon tissue (i, ii). Expression of BRD7 is markedly reduced in colon tumors, especially in the vasculature, and in general the expression is much more diffuse (iii, iv). Negative control staining is shown in panel v. Boxed areas are magnified in their respective panels below. For indicative purposes, several blood vessels are indicated with arrowheads. Scale bar = 100 µm. d Distribution of staining intensities in colon tumors and normal colon samples (N = 12) reported in The Protein Atlas indicates less intense staining in tumor tissues. e BRD7 mRNA expression is reduced in the (chicken derived) vasculature of different human tumors (colon, breast and ovary) xenografted on the CAM (Tumor CAM) in comparison with developmental CAM (Ctrl CAM), as determined by qPCR using chicken-specific primers. **p < 0.01 ANOVA. All data are presented as mean ± SEM
