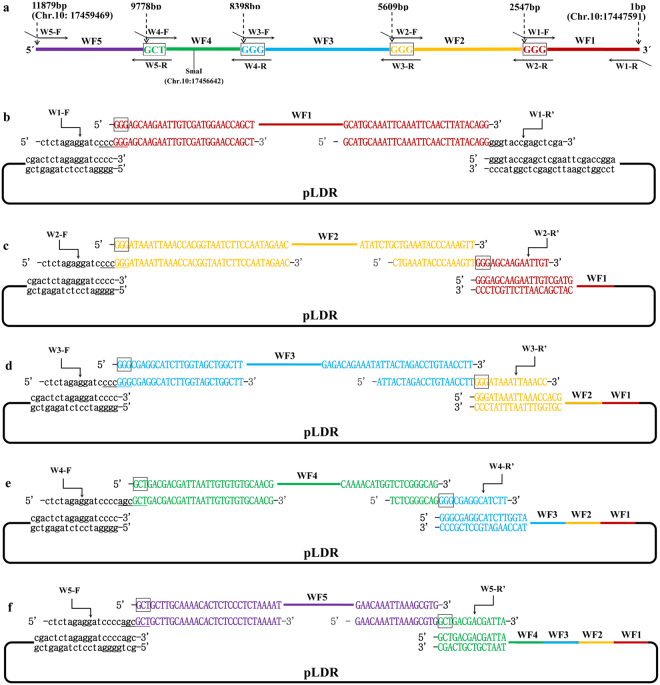
Figure 6.
Assembly of the 11.88 kb DNA molecule by changing assembly entrance in the assembly process. The stitching sites GGG and GCT are boxed. The line and sequence shown in black represent pLDR, red represents the first fragment of WF1, orange represents the second fragment of WF2, blue represents the third fragment of WF3, green represents the fourth fragment of WF4, and purple represents the fifth fragment of WF5. The primer of W1-R′ was reverse complement with W1-R, as well as W2- R′ and W2-R, W3- R′ and W3-R, W4- R′ and W4-R, W5- R′ and W5-R. (a) The 11.88 kb DNA molecule was divided into five fragments by three stitching sites GGG and one stitching site GCT. (b) The first round of assembly reaction for inserting WF1. The pLDR was digested by SmaI. When WF1 was assembled into pLDR, there was only 1 SmaI site in the assembly products, which can be cut to generate the assembly entrance for the second round. (c) The second round of assembly reaction for inserting WF2. The pLDR-WF1 was digested by SmaI. As for the first stitching site GGG in W2-R′, WF2 must join together with WF1 seamlessly, and then there is only 1 SmaI site in the second round of assembled products. (d) The third round of assembly reaction for inserting WF3. The pLDR-WF1 ~ WF2 was digested by SmaI. As for the second stitching site GGG in W3-R′, WF3 must join together with WF2 seamlessly, and then there is only 1 SmaI site in the third round of assembled products. (e) The fourth round of assembly reaction for inserting WF4. The pLDR-WF1 ~ WF3 was digested by SmaI. An Eco47III was introduced by adding AGC additionally in the overlapping region of W4-F before the stitching site GCT. As for the third stitching site GGG in W4-R′, WF4 must join together with WF3 seamlessly, and then there is only 1 Eco47III site in the fourth round of assembled products. (f) The fifth round of assembly reaction for inserting WF5. The pLDR-WF1~WF4 was digested by Eco47III. The fifth fragment of WF5 seamlessly joins with WF4.