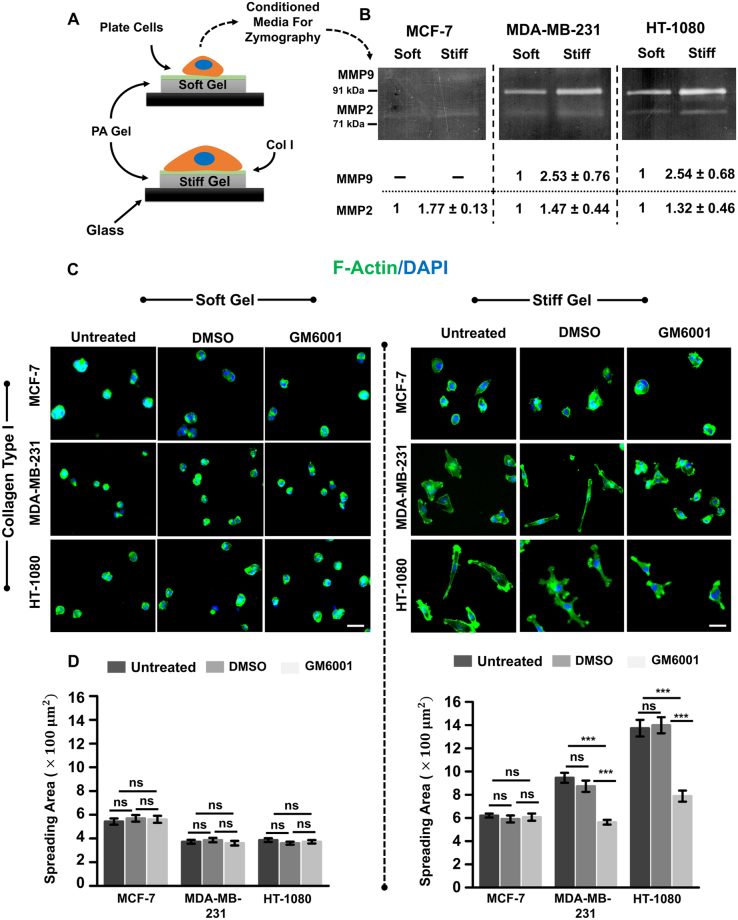
Figure 1.
Influence of MMP inhibition on stiffness-dependent cell spreading. (A) MCF-7, MDA-MB-231 and HT-1080 cells were cultured sparsely on collagen type I-coated soft and stiff polyacrylamide (PA) hydrogels for desired time duration. (B) Assessment of stiffness-dependent activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) (MMP 2, and 9) using gelatin zymography. Conditioned medium was collected after 30 hrs of incubation. Densitometric quantification of secretion levels of soluble MMPs in conditioned media by MCF-7, MDA-MB-231 and HT-1080 cells seeded on soft and stiff substrates reveals increase in MMP activity on stiffer gels (n = 2). (C) Representative F-actin (green) and DAPI (blue) stained images of untreated, DMSO treated and GM6001 treated MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, and HT-1080 cells seeded on soft and stiff gels. Scale bar = 50 μm. (D) Quantitative analysis of cell spreading of untreated, DMSO treated and GM6001 (GM) treated MCF-7, MDA-MB-231 and HT-1080 cancer cells seeded on soft and stiff gels (n = 2–3, at least 90–140 cells per condition). Stars denote statistical significance (***p < 0.001, ns: not significant). Statistical significance was determined using Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA/Mann-Whitney test. Error bars represent standard error of mean (±SEM).